Sketchtopia: A Dataset and Foundational Agents for Benchmarking Asynchronous Multimodal Communication with Iconic Feedback
|
[Paper] [CVPR Paper] [Dataset (WIP)] [Demo ]
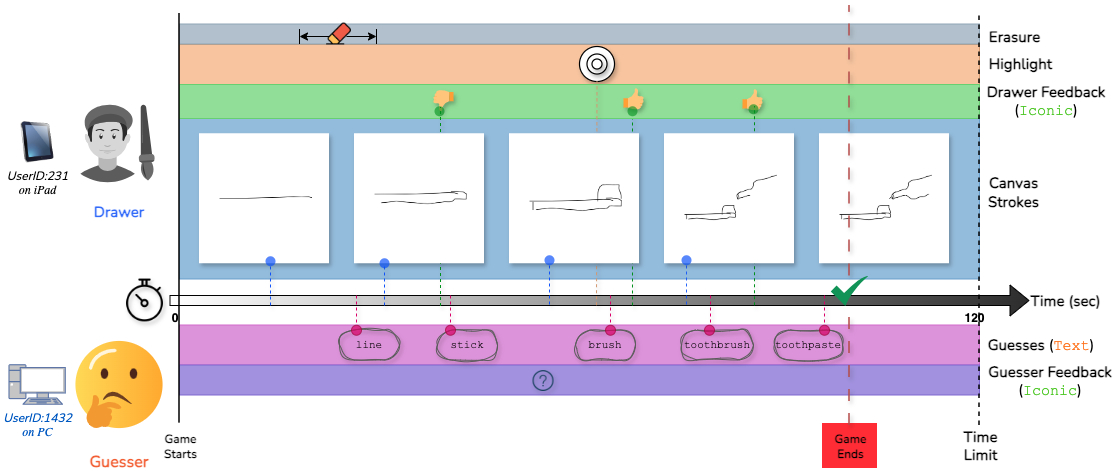
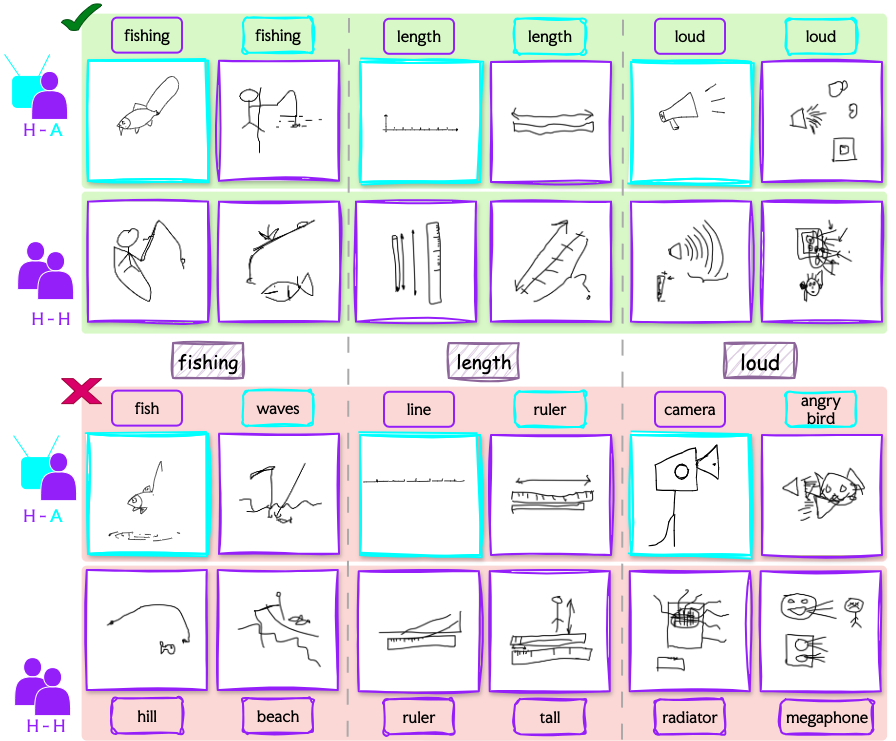
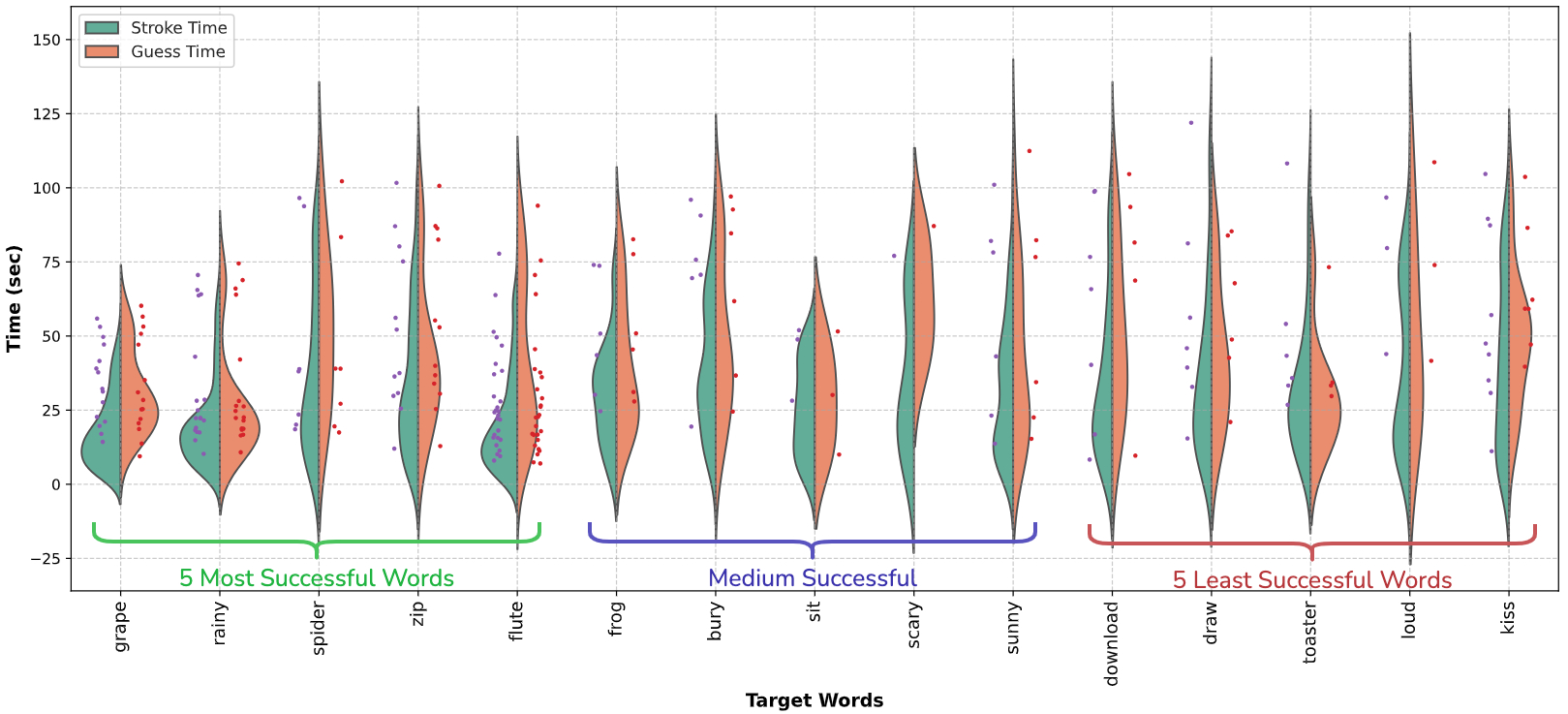

Figure. Illustration of a driving scenario where the ADAS vehicle predicts a left lane change (what) to avoid slower traffic ahead (why). Existing DIP models lacking reasoning may miss such cues, while our framework jointly learns and distills both maneuver and explanation, improving decision quality.
Abstract
Predicting a drivers’ intent (e.g., turns, lane changes) is a critical capability for modern Advanced Driver Assistance Prev. DIP: Only Intent Prediction (What Maneuver) Our DIP: Intent Prediction (What Maneuver) with Explanation (Why) (what) Left Lane Change Systems (ADAS). While recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) show promise in general vision-language tasks, we find that zeroshot MLLMs still lag behind domain specific approaches for Driver Intention Prediction (DIP). To address this, we introduce DriveXplain, a zero-shot framework based on MLLMs that leverages rich visual cues such as optical flow and road semantics to automatically generate both intention maneuver (what) and rich natural language explanations (why). These maneuver–explanation pairs are then distilled into a compact MLLM, which jointly learns to predict intentions and corresponding explanations. We show that incorporating explanations during training leads to substantial gains over models trained solely on labels, as distilling explanations instills reasoning capabilities by enabling the model to understand not only what decisions to make but also why those decisions are made. Comprehensive experiments across structured (Brain4Cars, AIDE) and unstructured (DAAD) datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results in DIP task, outperforming zero-shot and domain-specific baselines. We also present ablation studies to evaluate key design choices in our framework. This work sets a direction for more explainable and generalizable intention prediction in autonomous driving systems. We plan to release our codebase to support research.
Methodology
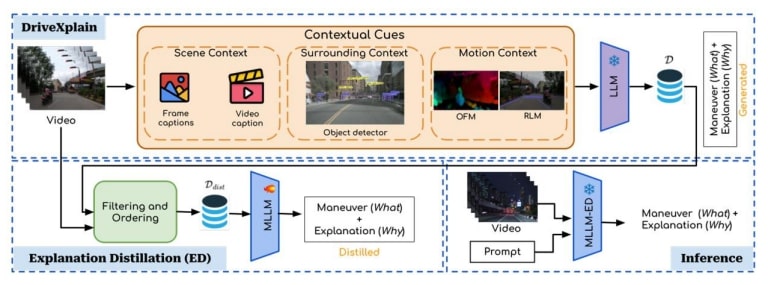
Figure. Our proposed framework for the DIP task. DriveXplain generates natural language explanations alongside maneuvers and Explanation Distillation distills these explanations into a single MLLM to enhance DIP performance at inference.
Key Highlights:
- New Task: Understanding why a driver makes a decision is just as important as predicting what they’ll do next.
- DriveXplain Model: We introduce a zero-shot framework that enhances MLLMs for ADAS by embedding driving-specific context directly into their reasoning.
- Knowledge Distillation: To enable real-time, deployable solutions, we distill reasoning and decision-making capabilities from large MLLMs into smaller, efficient models — paving the way for explainable driving intelligence.
Results
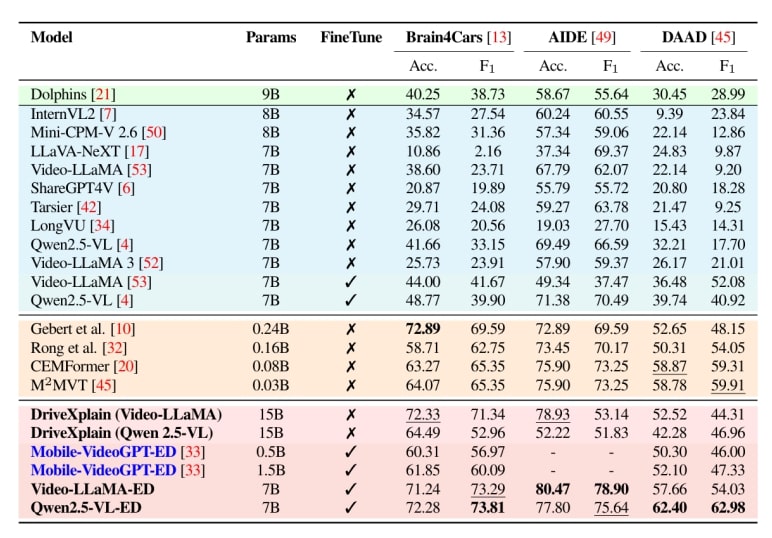
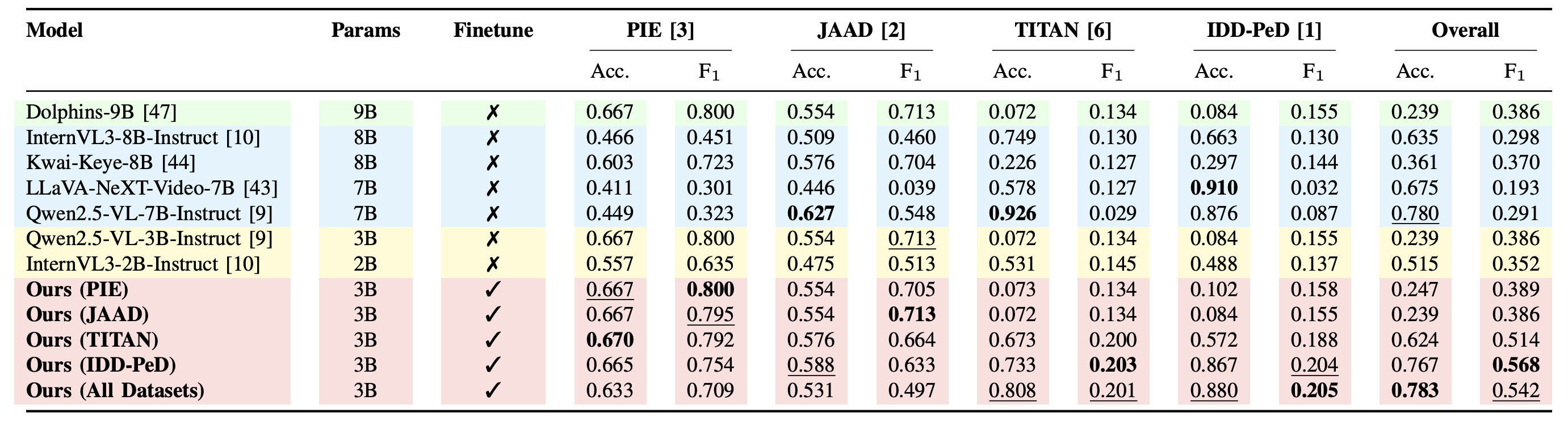
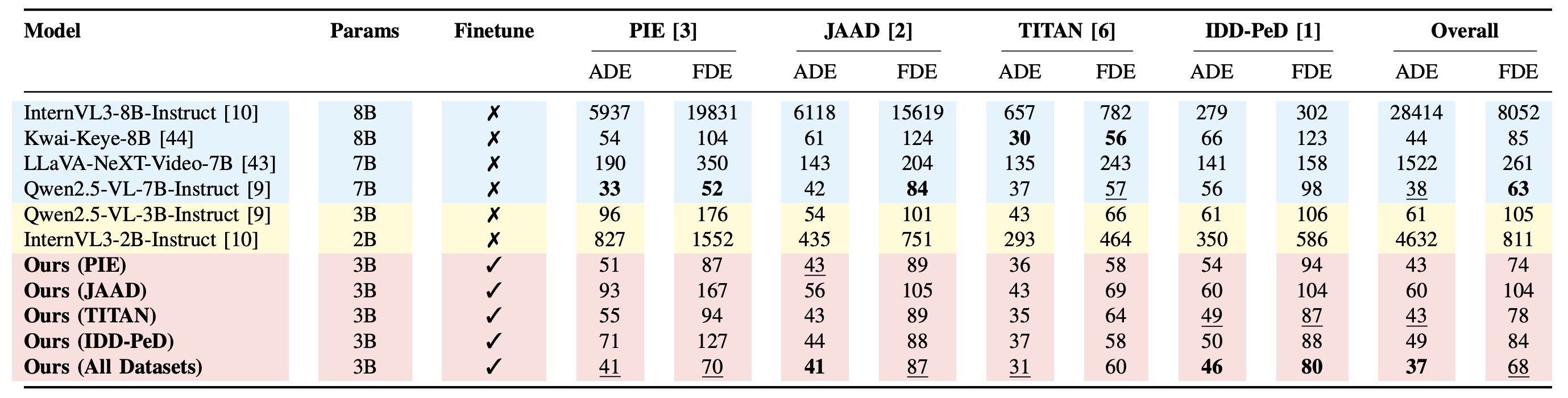
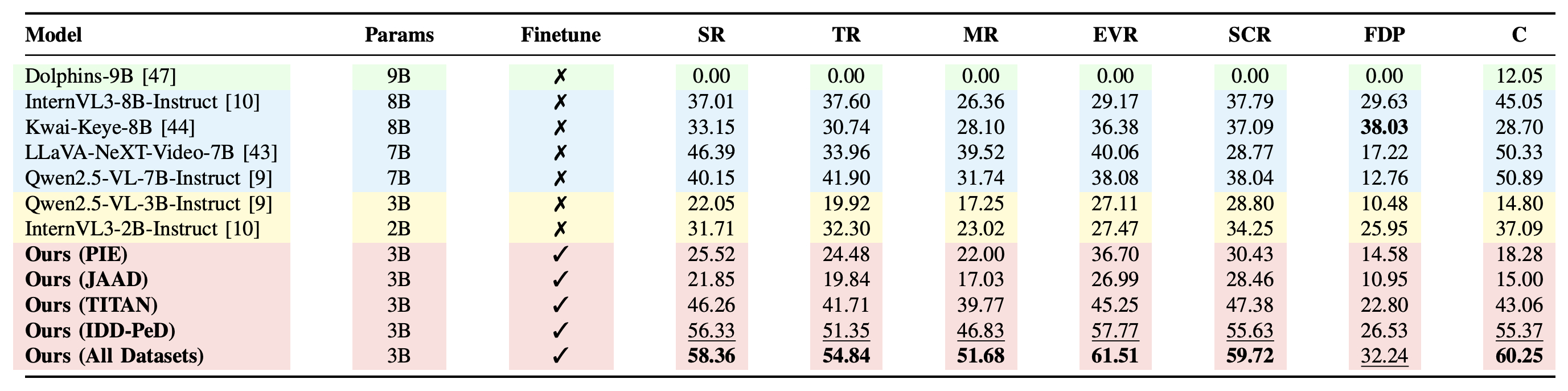
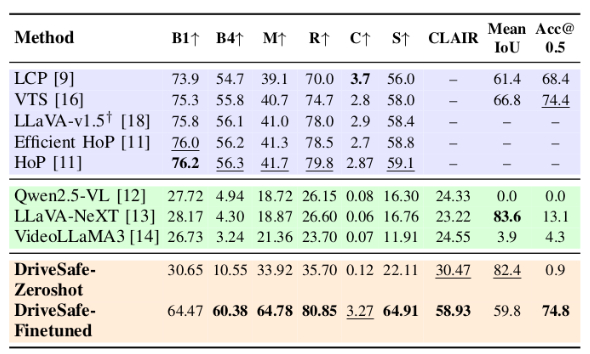
Table DIP benchmark results. Performance comparison of Driving-specific VLM, General VLMs, Action Anticipation models, and our framework (DriveXplain, ED).Accuracy (Acc.) and F1 (%) on Brain4Cars AIDE, and DAAD datasets. Finetune indicates whether the model was fine-tuned (✓) or evaluated in a zero-shot (✗) setting. Bold and underline indicate the best and second-best results.
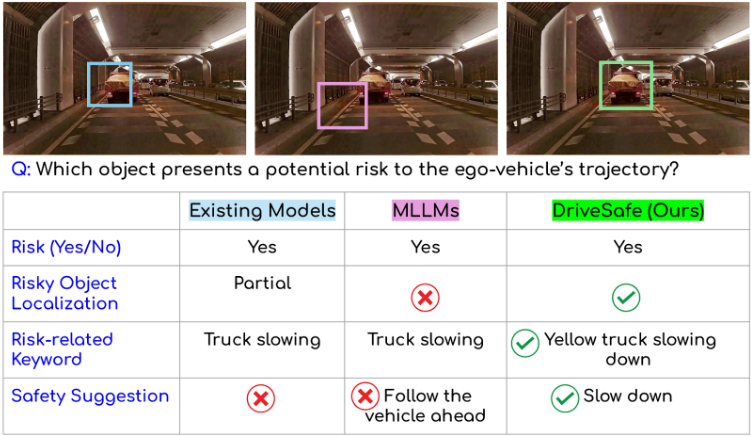
Figure: Qualitative comparison of proposed framework, zero-shot Qwen2.5-VL, Dolphins across Brain4cars, AIDE, and DAAD datasets. We show manoeuvre prediction (what) and explanation (why), with attention heatmaps highlighting key regions.
Citation
@in proceedings{vcbm2025daadx,
author = {Sainithin Artham, Avijit Dasgupta, Shankar Gangisetty, and C. V. Jawahar},
title = {Distilling What and Why: Enhancing Driver Intention Prediction w
ith MLLMs},
booktitle = {},
series = {},
volume = {},
pages = {},
publisher = {},
year = {2025},
}
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by iHub-Data and Mobility at IIIT Hyderabad.