Fine Pose Estimation of Known Objects from a Single Scene Image
Introduction
Understanding the precise 3D structure of an environ- ment is one of the fundamental goals of computer vision and is challenging due to a variety of factors such as ap- pearance variation, illumination, pose, noise, occlusion and scene clutter. A generic solution to the problem is ill-posed due to the loss of depth information during imaging. In this paper, we consider a specific but common situation, where the scene contains known objects. Given 3D models of a set of known objects and a cluttered scene image, we try to detect these objects in the image, and align 3D models to their images to find their exact pose. We develop an ap- proach that poses this as a 3D-to-2D alignment problem. We also deal with pose estimation of 3D articulated objects in images. We evaluate our proposed method on BigBird dataset and our own tabletop dataset, and present experi- mental comparisons with state-of-the-art methods.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The idea of the problem is given a single cluttered scene image, is it possible to find the pose of objects in it. As observed, our method is robust to objects of various shape, sizes and texture and also in terms of object-object occlusion.
We build on previous approaches like Jim et el. [2] and Aubry et al. [3]. Jim et al. use a user-driven set of 2D-to-3D correspondences to extract geometric cues to refine the correspondence set to obtain the pose using ICP. Aubry et al. on the other hand, use whitened HoG as discriminative features to select the closest matching image from a set of rendered viewpoints as the final pose. Hence, the final pose is dependant on the sampling of the camera viewpoints. Our goal differs from the above primarily in its assumptions about the objects and their models. We try to find the pose of common tabletop objects that could potentially be low-lying and the models are assumed to be without any texture, making the alignment problem hard. Our major contributions include: 1) An ensemble of shape features that work well for aligning textureless 3D models, 2) A two- stage alignment scheme that is efficient and accurate and 3) An extension of the proposed approach to handle articulated objects. We demonstrate our results on a variety of tabletop objects including transparent ones and scene images with occlusion and background clutter. Note that textureless 3D models are used to generalize our proposed method to objects that are very similar in shape and size, but vary in texture. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art method for pose estimation.
Method Overview
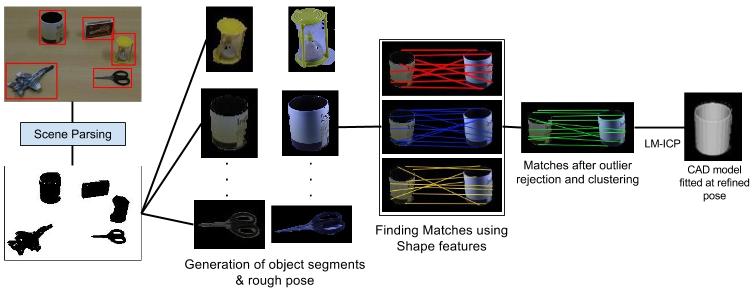
Dataset
We evaluate our proposed method on BigBird [4] dataset and our own dataset of common household objects: TableTop. Both BigBird and TableTop contains RGB images of a single object at various orientations, captured under controlled environment. Additionally, TableTop dataset contains cluttered scene images having multiple objects having occlusion constraints. The dataset statistics are given below:
BigBird:
For each object, images are captured at an azimuth interval of 3° and elevation interval of 18°, making a total of 120 images per elevation angle.
Number of objects: 15
Number of images per object: 600
Total: 9000
TableTop:
For each object, images are captured at an azimuth interval of 100 and at elevations of 0°, 15°, 30°, 45°, and 60°, and one image from 90° elevation.
Number of objects: 50
Number of images per object: 181
Total: 9050
Results and Comparisons
Qualitative Results:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Top row: Input scene images Bottom row: Scene images with 3D model poses. Models corresponding to the objects are fetched from the repository and superimposed with their correct pose.
Quantitative Results:
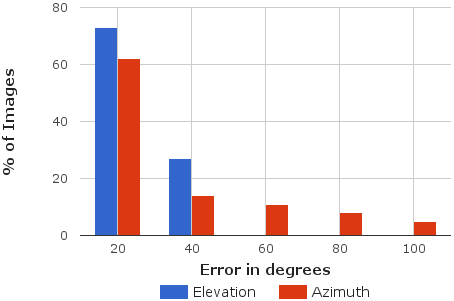 |
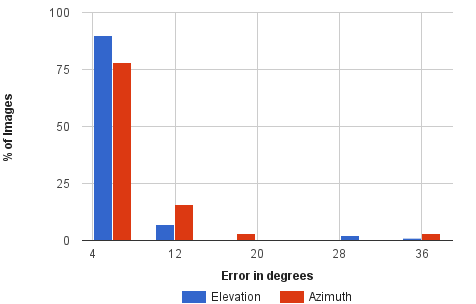 |
| Left: Error in initial hypothesis. Right: Error in refined pose. As observed, out method refines upto 6° of groundtruth for 80% of the examples. | |
Qualitative Comparison:
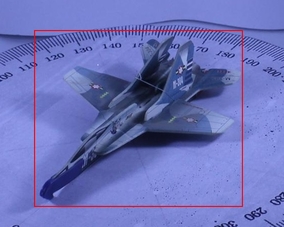 |
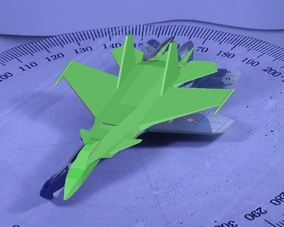 |
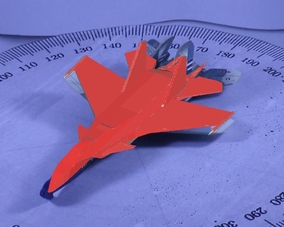 |
 |
 |
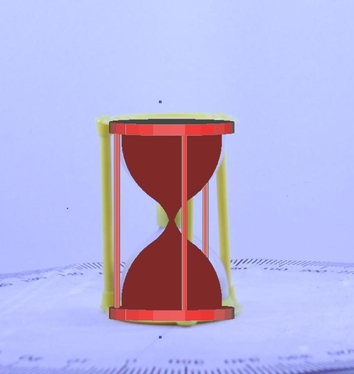 |
Qualitative comparison of proposed method with S3DC. As observed from the figure, proposed method is able to provide a more refined pose compared to S3DC.
Qualitative Comparison:
| Transparent Bottle | Sand Clock | Pen Stand | Scissors | Spectacles Case | ||||||
| Accuracy (%) | MPE | Accuracy (%) | MPE | Accuracy (%) | MPE | Accuracy (%) | MPE | Accuracy (%) | MPE | |
| S3DC | 31.11 | 0.147 | 83.33 | 0.086 | 91.11 | 0.093 | 6.67 | 0.4 | 44.44 | 0.016 |
| Ours | 83.52 | 0.0016 | 86.81 | 0.033 | 83.52 | 0.002 | 73.63 | 0.086 | 54.65 | 0.121 |
We compare the classification accuracy and mean pose error (MPE) with S3DC, for some of the objects from our dataset with varying complexity in terms of shape, size and material.
| BigBird | TableTop | |||
| Accuracy (%) | MPE | Accuracy (%) | MPE | |
| S3DC | 34.5 | 0.013 | 45.7 | 0.044 |
| Ours | 49.7 | 0.008 | 67.3 | 0.021 |
We compare the classification accuracy and mean pose error (MPE) with S3DC, for some of the objects from our dataset with varying complexity in terms of shape, size and material.
Related Publications
Sudipto Banerjee, Sanchit Aggarwal, Anoop M. Namboodiri - Fine Pose Estimation of Known Objects in Cluttered Scene Images Proceedings of the 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, 03-06 Nov 2015, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. [PDF]
- M. Aubry, D. Maturana, A. A. Efros, B. C. Russell, and J. Sivic - Seeing 3d chairs: exemplar part-based 2d-3d alignment using a large dataset of cad models Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014. [PDF]
- J. J. Lim, H. Pirsiavash, and A. Torralba - Parsing ikea objects: Fine pose estimation International Conference on Computer Vision, 2013. [PDF]
- A. Singh, J. Sha, K. S. Narayan, T. Achim, and P. Abbeel - Bigbird: A large-scale 3d database of object instances International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2014. [PDF]
Code and Dataset
- Code: To be updated soon
- BigBird dataset can be downloaded from here
- TableTop dataset can be downloaded here
Associated People