List of Projects
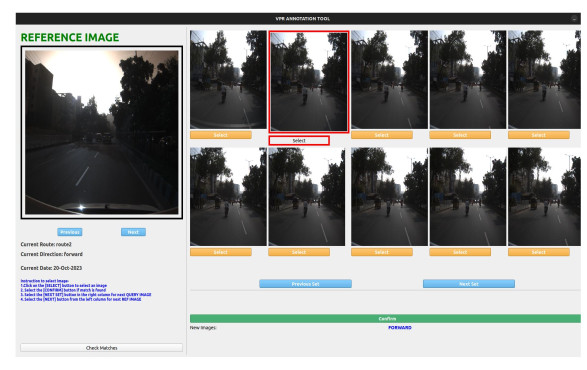 Visual Place Recognition in Unstructured Driving Environments
Visual Place Recognition in Unstructured Driving Environments
People Involved : Utkarsh Rai, Shankar Gangisetty, A. H. Abdul Hafez, Anbumani Subramanian and C V Jawahar
The problem of determining geolocation through visual inputs, known as Visual Place Recognition (VPR), has attracted significant attention in recent years owing to its potential applications in autonomous self-driving systems.
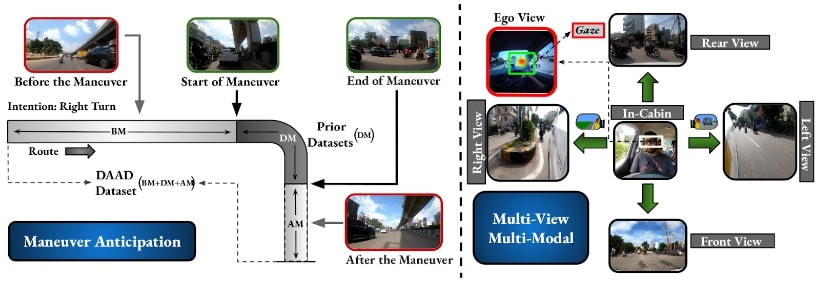 Early Anticipation of Driving Maneuvers
Early Anticipation of Driving Maneuvers
People Involved : Abdul Wasi, Shankar Gangisetty, Shyam Nanadan and C V Jawahar
Prior works have addressed the problem of driver intention prediction (DIP) to identify maneuvers post their onset. On the other hand, early anticipation is equally important in scenarios that demand a preemptive response before a maneuver begins.
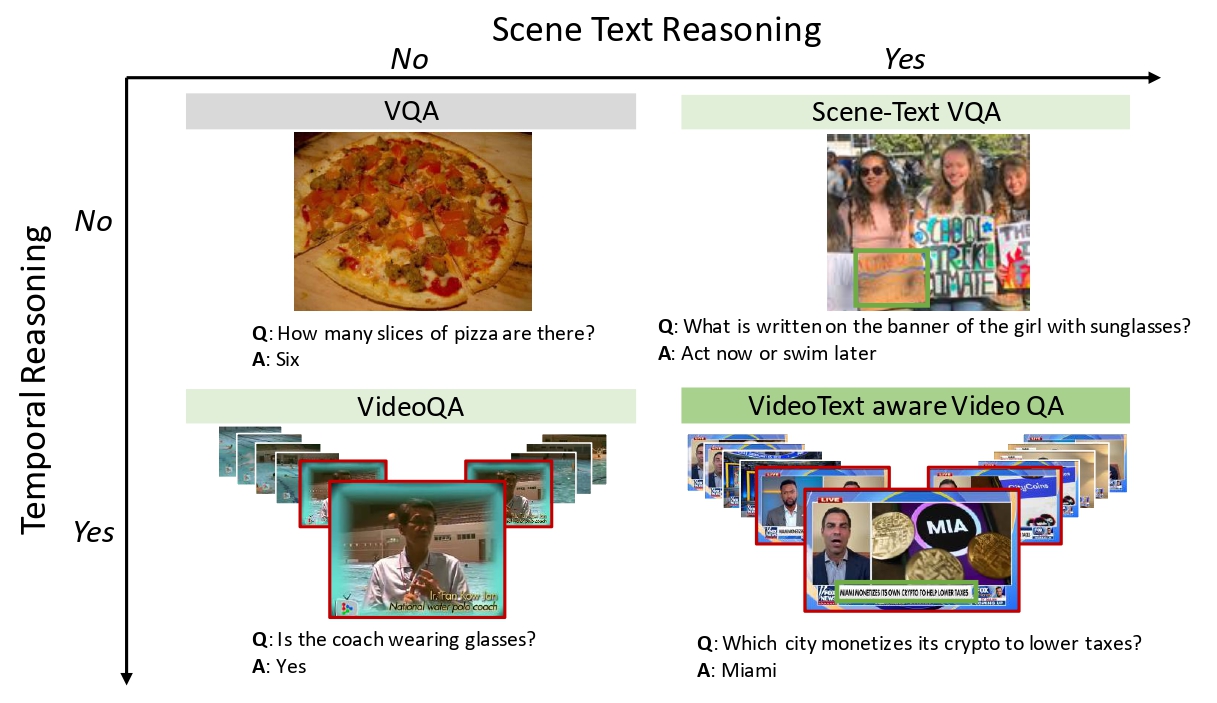 Watching the News: Towards VideoQA Models that can Read
Watching the News: Towards VideoQA Models that can Read
People Involved : Soumya Jahagirdar, Minesh Mathew, Dimosthenis Karatzas, C. V. Jawahar
Video Question Answering methods focus on commonsense reasoning and visual cognition of objects or persons and their interactions over time. Current VideoQA approaches ignore the textual information present in the video. Instead, we argue that textual information is complementary to the action and provides essential contextualisationcues to the reasoning process.
People Involved : Madhav Agarwal, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
In this paper, This work proposes a novel method to generate realistic talking head videos using audio and visual streams. We animate a source image by transferring head motion from a driving video using a dense motion field generated using learnable keypoints. We improve the quality of lip sync using audio as an additional input, helping the network to attend to the mouth region.
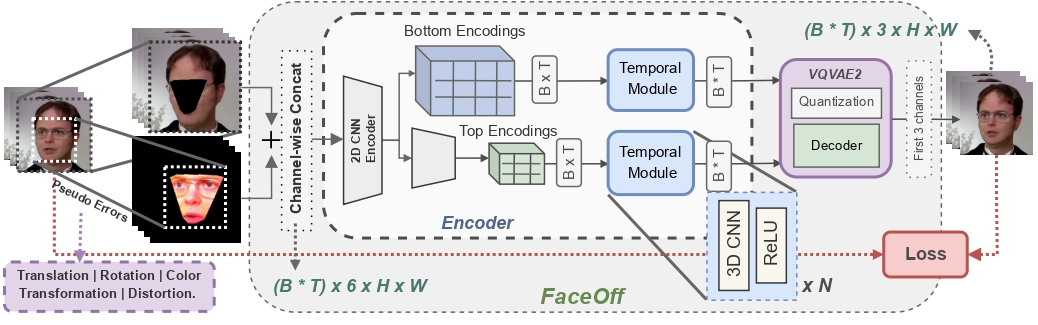 FaceOff: A Video-to-Video Face Swapping System
FaceOff: A Video-to-Video Face Swapping System
People Involved : Aditya Agarwal*, Bipasha Sen*, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay P Namboodiri, C. V. Jawahar
Doubles play an indispensable role in the movie industry. They take the place of the actors in dangerous stunt scenes or scenes where the same actor plays multiple characters. The double's face is later replaced with the actor's face and expressions manually using expensive CGI technology,
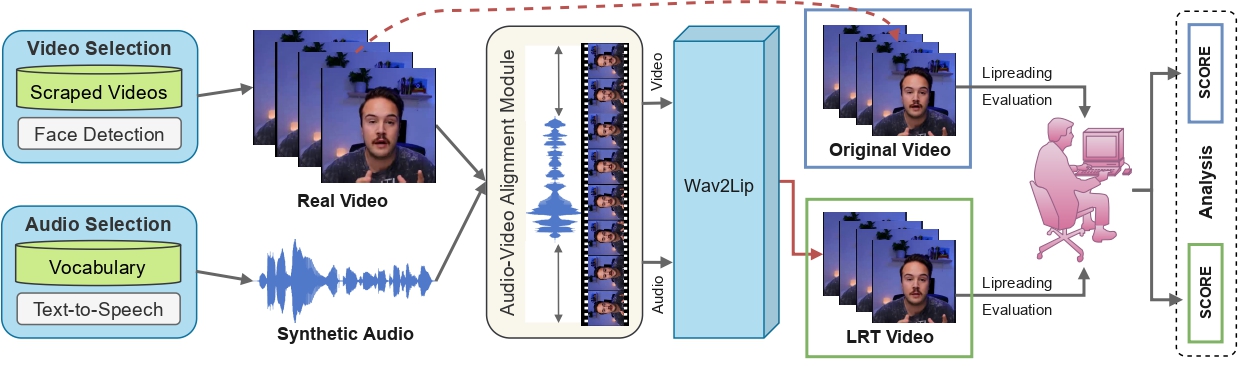 Towards MOOCs for Lipreading: Using Synthetic Talking Heads to Train Humans in Lipreading at Scale
Towards MOOCs for Lipreading: Using Synthetic Talking Heads to Train Humans in Lipreading at Scale
People Involved : Aditya Agarwal*, Bipasha Sen*, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay P Namboodiri, C. V. Jawahar
Many people with some form of hearing loss consider lipreading as their primary mode of day-to-day communication. However, finding resources to learn or improve one's lipreading skills can be challenging.
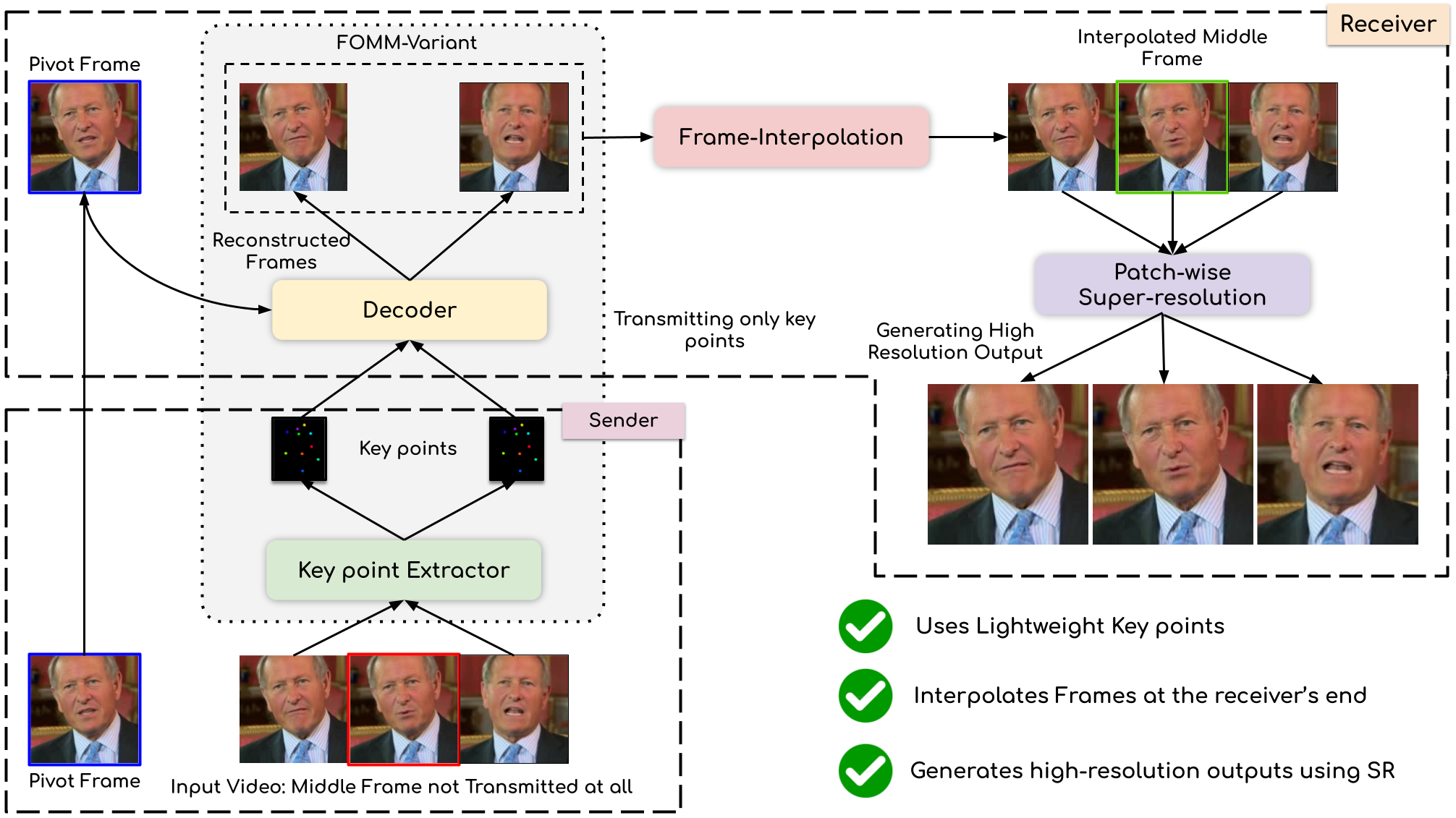 Compressing Video Calls using Synthetic Talking Heads
Compressing Video Calls using Synthetic Talking Heads
People Involved : Madhav Agarwal, Anchit Gupta, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
We leverage the modern advancements in talking head generation to propose an end-to-end system for talking head video compression. Our algorithm transmits pivot frames intermittently while the rest of the talking head video is generated by animating them. We use a state-of-the-art face reenactment network to detect key points in the non-pivot frames and transmit them to the receiver.
 Unsupervised Audio-Visual Lecture Segmentation
Unsupervised Audio-Visual Lecture Segmentation
People Involved : Darshan Singh S*, Anchit Gupta*, C.V. Jawahar and Makarand Tapaswi
This Over the last decade, online lecture videos have become increasingly popular and have experienced a meteoric rise during the pandemic. However, video-language research has primarily focused on instructional videos or movies, and tools to help students navigate the growing online lectures are lacking....
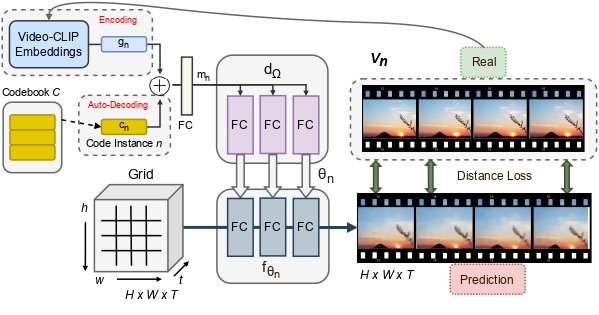 INR-V: A Continuous Representation Space for Video-based Generative Tasks
INR-V: A Continuous Representation Space for Video-based Generative Tasks
People Involved : Bipasha Sen, Aditya Agarwal, Vinay P Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
Generating videos is a complex task that is accomplished by generating a set of temporally coherent images frame-by-frame. This limits the expressivity of videos to only image-based operations on the individual video frames needing network designs to obtain temporally coherent trajectories in the underlying image space. We propose INR-V, a video representation network that learns a continuous space for video-based generative tasks.
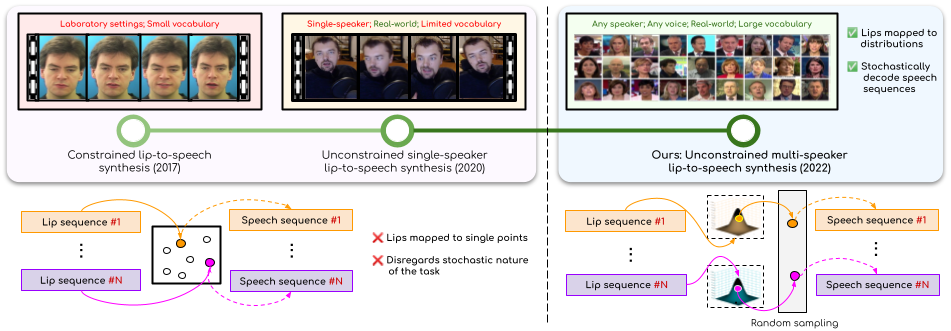 Lip-to-Speech Synthesis for Arbitrary Speakers in the Wild
Lip-to-Speech Synthesis for Arbitrary Speakers in the Wild
People Involved : Sindhu B Hegde, K R Prajwal, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
In this work, we address the problem of generating speech from silent lip videos for any speaker in the wild. In stark contrast to previous works in lip-to-speech synthesis, our work (i) is not restricted to a fixed number of speakers, (ii) does not explicitly impose constraints on the domain or the vocabulary and (iii) deals with videos that are recorded in the wild as opposed to within laboratory settings.
 Extreme-scale Talking-Face Video Upsampling with Audio-Visual Priors
Extreme-scale Talking-Face Video Upsampling with Audio-Visual Priors
People Involved : Sindhu B Hegde, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
In this paper, we explore an interesting question of what can be obtained from an 8×8 pixel video sequence. Surprisingly, it turns out to be quite a lot. We show that when we process this 8x8 video with the right set of audio and image priors, we can obtain a full-length, 256x256 video. We achieve this 32x scaling of an extremely low-resolution input using our novel audio-visual upsampling network
 My View is the Best View: Procedure Learning from Egocentric Videos
My View is the Best View: Procedure Learning from Egocentric Videos
People Involved : Siddhant Bansal , Chetan Arora and C.V. Jawahar
Using third-person videos for procedure learning makes the manipulated object small in appearance and often occluded by the actor, leading to significant errors. In contrast, we observe that videos obtained from first-person (egocentric) wearable cameras provide an unobstructed and clear view of the action.
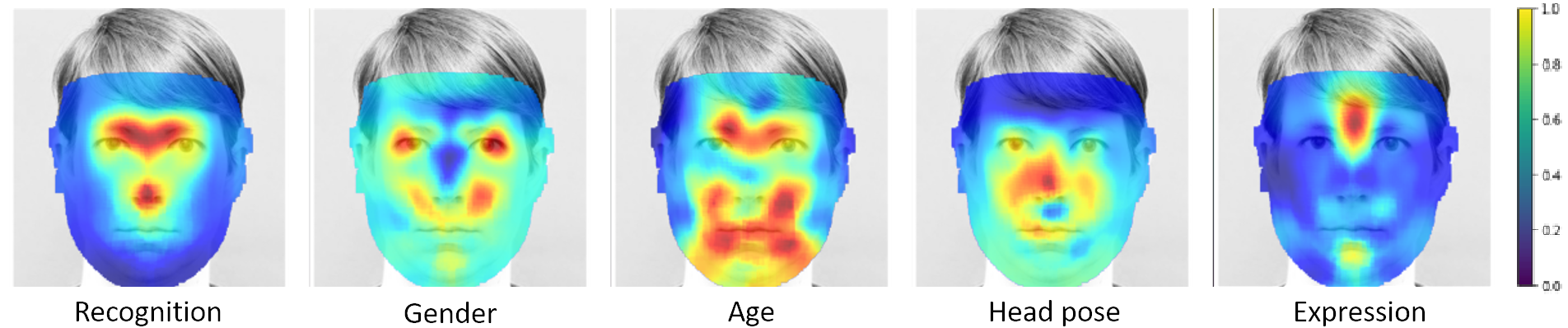 Canonical Saliency Maps: Decoding Deep Face Models
Canonical Saliency Maps: Decoding Deep Face Models
People Involved : Thrupthi Ann John, Vineeth N Balasubramanian and C. V. Jawahar
As Deep Neural Network models for face processing tasks approach human-like performance, their deployment in critical applications such as law enforcement and access control has seen an upswing, where any failure may have far-reaching consequences.
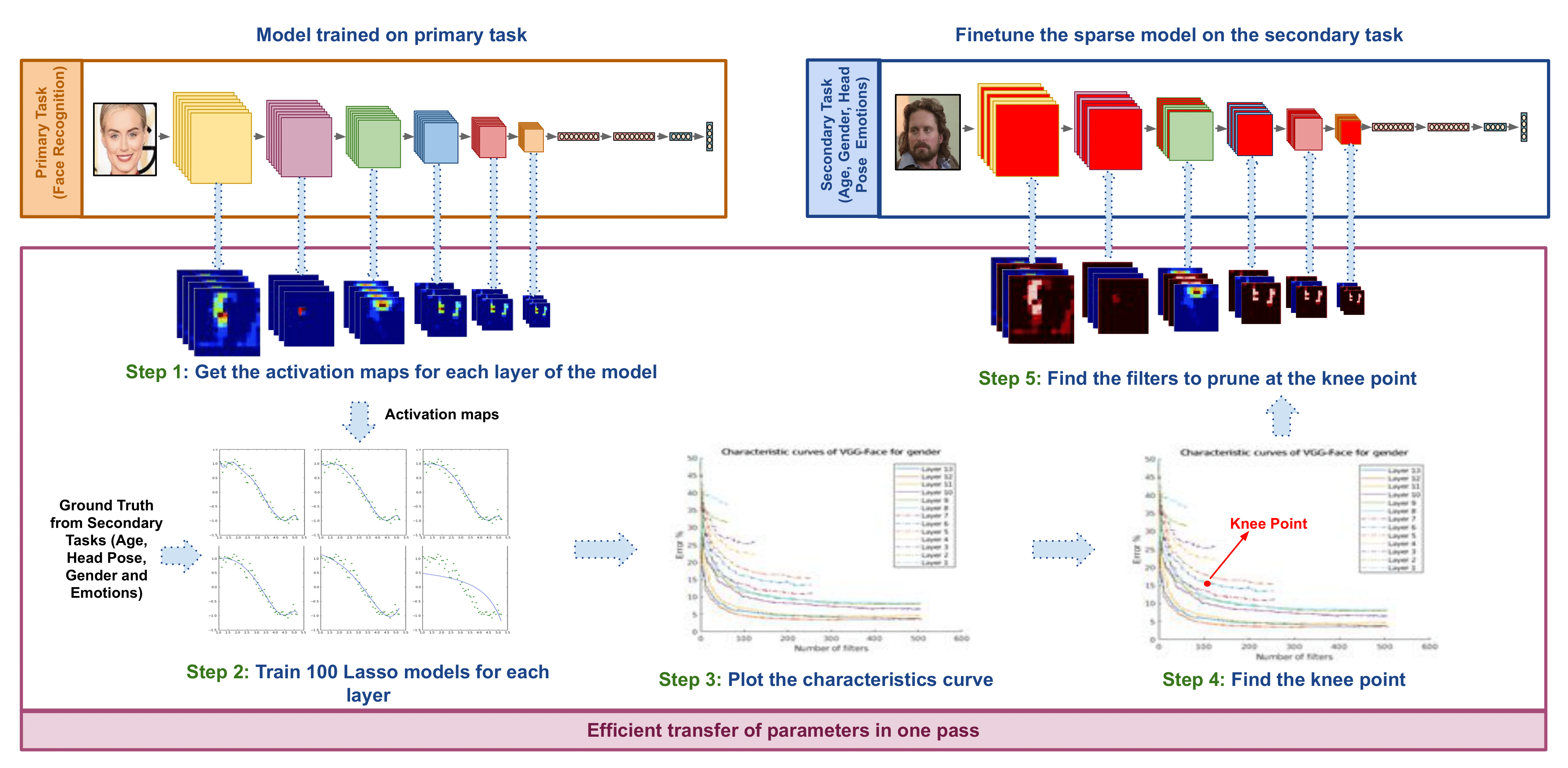 ETL: Efficient Transfer Learning for Face Tasks
ETL: Efficient Transfer Learning for Face Tasks
People Involved : Thrupthi Ann John,Isha Dua, Vineeth N Balasubramanian and C. V. Jawahar
ransfer learning is a popular method for obtaining deep trained models for data-scarce face tasks such as head pose and emotion. However, current transfer learning methods are inefficient and time-consuming as they do not fully account for the relationships between related tasks..
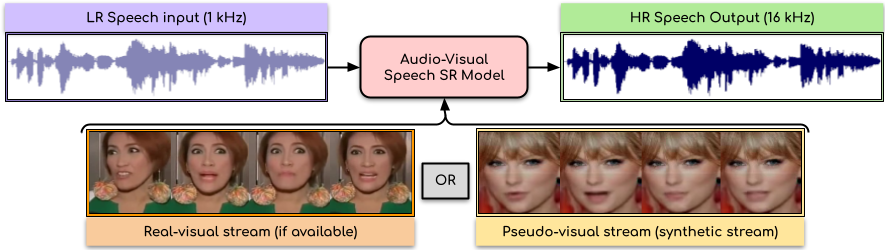 Audio-Visual Speech Super-Resolution
Audio-Visual Speech Super-Resolution
People Involved : Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Sindhu Hegde Vinay Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
In this paper, we present an audio-visual model to perform speech super-resolution at large scale-factors (8x and 16x). Previous works attempted to solve this problem using only the audio modality as input and thus were limited to low scale-factors of $2\times$ and $4\times$. In contrast, we propose to incorporate both visual and auditory signals to super-resolve speech of sampling rates as low as $1$kHz.
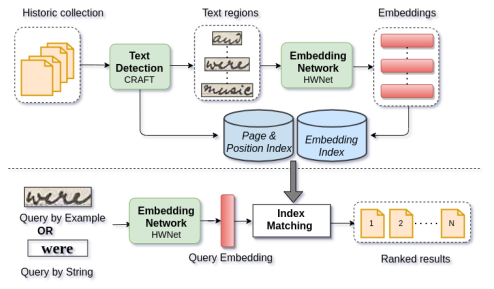 Handwritten Text Retrieval from Unlabeled Collections
Handwritten Text Retrieval from Unlabeled Collections
People Involved : Santhoshini Gongid and C.V. Jawahar
Handwritten documents from communities like cultural heritage, judiciary, and modern journals remain largely unexplored even today. To a great extent, this is due to the lack of retrieval tools for such unlabeled document collections. In this work, we consider such collections and present a simple, robust retrieval framework for easy information access. We achieve retrieval on unlabeled novel collections through invariant features learnt for handwritten text. These feature representations enable zero-shot retrieval for novel queries on unexplored collections.

People Involved : Jobin K.V., Ajoy Mondal, and Jawahar C.V.
Slide presentations are an effective and efficient tool used by the teaching community for classroom communication. However, this teaching model can be challenging for the blind and visually impaired (VI) students. The VI student required a personal human assistance for understand the presented slide. This shortcoming motivates us to design a Classroom Slide Narration System (CSNS) that generates audio descriptions corresponding to the slide content. This problem poses as an image-to-markup language generation task. The initial step is to extract logical regions such as title, text, equation, figure, and table from the slide image.
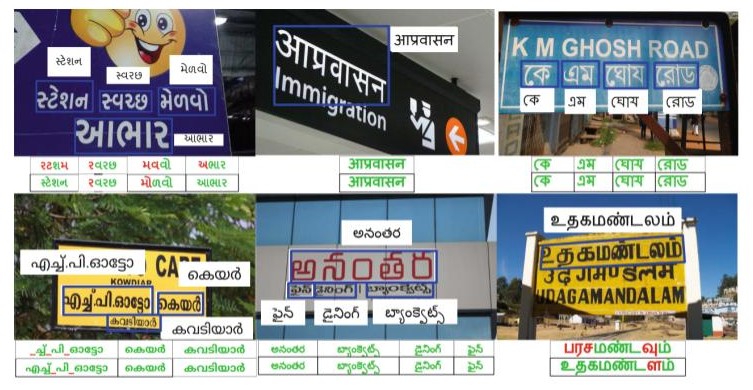 Transfer Learning for Scene Text Recognition in Indian Languages
Transfer Learning for Scene Text Recognition in Indian Languages
People Involved : Sanjana Gunna, Rohit Saluja, and C.V. Jawahar
Scene text recognition in low-resource Indian languages is challenging because of complexities like multiple scripts, fonts, text size, and orientations. In this work, we investigate the power of transfer learning for all the layers of deep scene text recognition networks from English to two common Indian languages.
 Towards Boosting the Accuracy of Non-Latin Scene Text Recognition
Towards Boosting the Accuracy of Non-Latin Scene Text Recognition
People Involved : Sanjana Gunna, Rohit Saluja, and C.V. Jawahar
Scene-text recognition is remarkably better in Latin languages than the non-Latin languages due to several factors like multiple fonts, simplistic vocabulary statistics, updated data generation tools, and writing systems.
People Involved : Zeeshan Khan, Kartheek Akella , Vinay Namboodiri C.V. Jawahar
This work studies the long-standing problems of model capacity and negative interference in multilingual neural machine translation (MNMT). We use network pruning techniques and observe that pruning 50-70% of the parameters from a trained MNMT model results only in a 0.29-1.98 drop in the BLEU score. Suggesting that there exist large redundancies even in MNMT models.
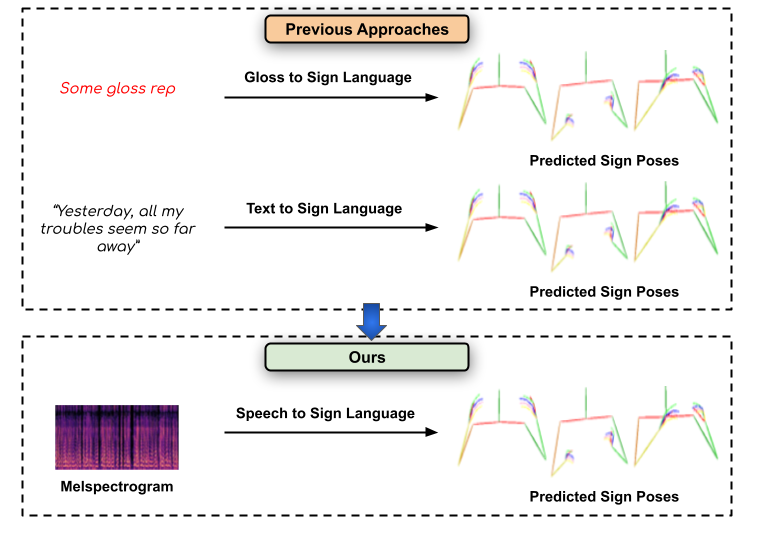 Towards Speech to Sign Language Generation
Towards Speech to Sign Language Generation
People Involved : Parul Kapoor, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay Sindhu B Hegde , Vinay Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
We aim to solve the highly challenging task of generating continuous sign language videos solely from speech segments for the first time. Recent efforts in this space have focused on generating such videos from human-annotated text transcripts without considering other modalities. However, replacing speech with sign language proves to be a practical solution while communicating with people suffering from hearing loss.
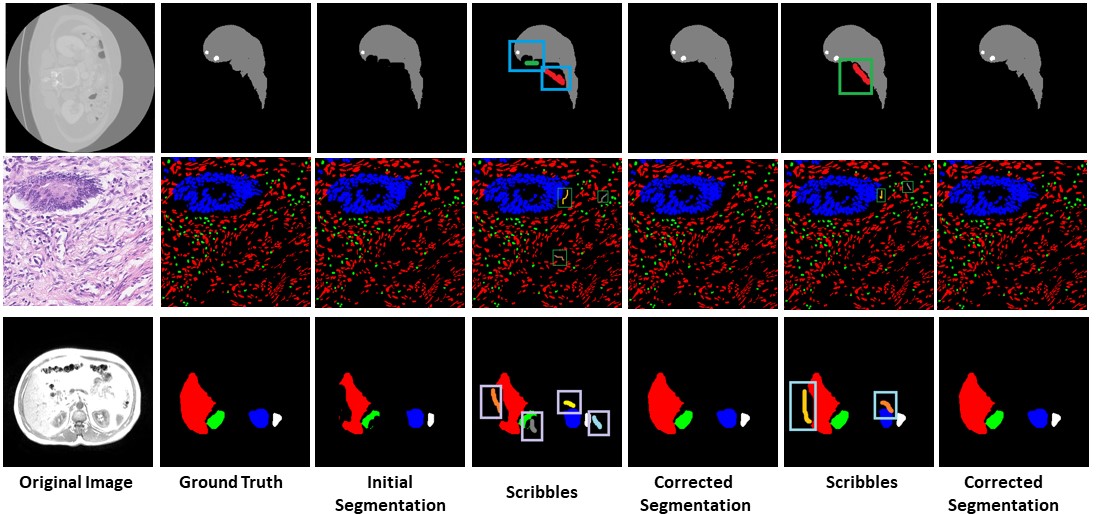 Semi-Automatic Medical Image Annotation
Semi-Automatic Medical Image Annotation
People Involved : Bhavani Sambaturu*, Ashutosh Gupta, C.V. Jawahar and Chetan Arora
Semantic segmentation of medical images is an essential first step in computer-aided diagnosis systems for many applications.
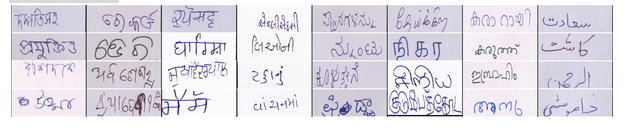 IIIT-INDIC-HW-WORDS: A Dataset for Indic Handwritten Text Recognition
IIIT-INDIC-HW-WORDS: A Dataset for Indic Handwritten Text Recognition
People Involved : Santhoshini Gongidi, and C V Jawahar
Handwritten text recognition for Indian languages is not yet a well-studied problem. This is primarily due to the unavailability of large annotated datasets in the associated scripts. Existing datasets are small in size. They also use small lexicons. Such datasets are not sufficient to build robust solutions to HTR using modern machine learning techniques. In this work, we introduce a large-scale handwritten dataset for Indic scripts, referred to as the IIIT-INDIC-HW-WORDS dataset.
 Scene Text Recognition in Indian Scripts
Scene Text Recognition in Indian Scripts
People Involved : Minesh Mathew, Mohit Jain and CV Jawahar
This work addresses the problem of scene text recognition in India scripts. As a first step, we benchmark scene text recognition for three Indian scripts - Devanagari, Telugu and Malayalam, using a CRNN model.
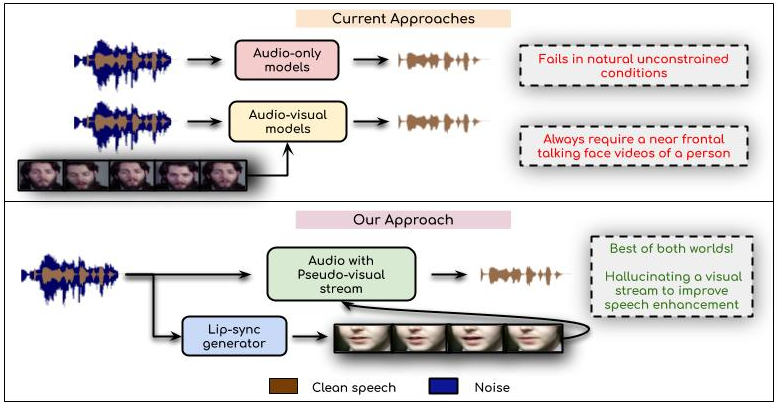 Visual Speech Enhancement Without a Real Visual Stream
Visual Speech Enhancement Without a Real Visual Stream
People Involved : Sindhu Hegde, Prajwal Renukanand, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay Namboodiri and C. V. Jawahar
In this work, we re-think the task of speech enhancement in unconstrained real-world environments. Current state-of-the-art methods use only the audio stream and are limited in their performance in a wide range of real-world noises.
 DGAZE Dataset for driver gaze mapping on road
DGAZE Dataset for driver gaze mapping on road
People Involved : Isha Dua Thrupthi John Riya Gupta and C.V. Jawahar
DGAZE is a new dataset for mapping the driver's gaze onto the road. Currently, driver gaze datasets are collected using eye-tracking hardware which are expensive and cumbersome, and thus unsuited for use during testing
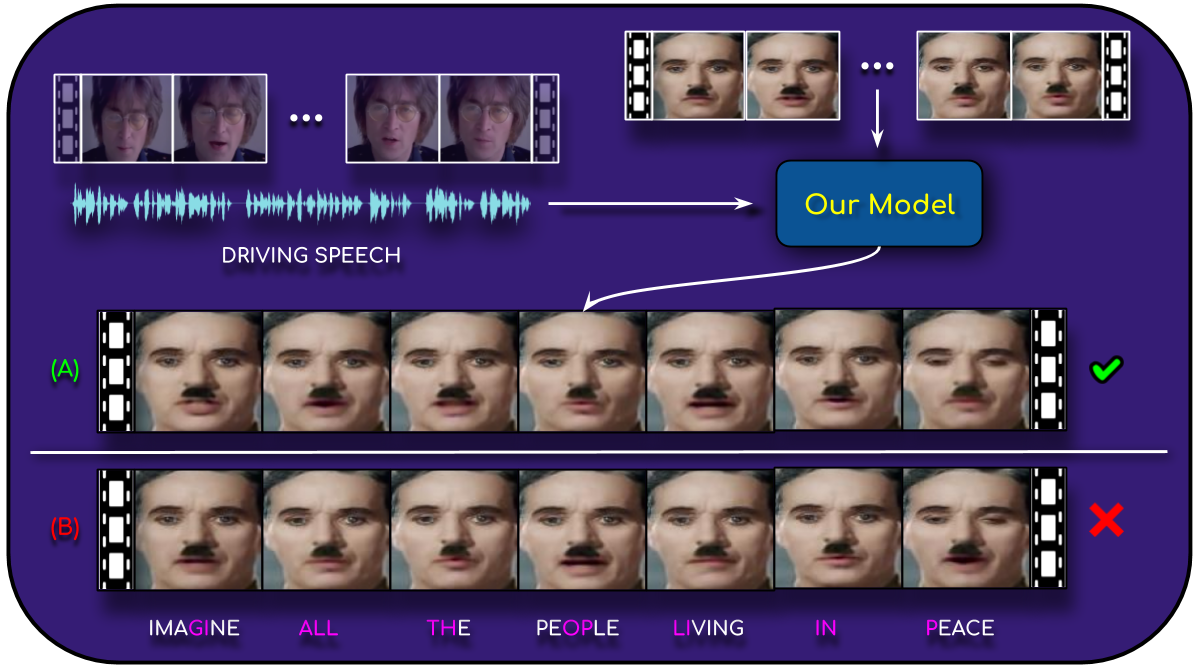 A Lip Sync Expert Is All You Need for Speech to Lip Generation In the Wild
A Lip Sync Expert Is All You Need for Speech to Lip Generation In the Wild
People Involved : Prajwal Renukanand, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay Namboodiri, and C.V. Jawahar
n this work, we investigate the problem of lip-syncing a talking face video of an arbitrary identity to match a target speech segment. Current works excel at producing accurate lip movements on a static image or on videos of specific people seen during the training phase. However, they fail to accurately morph the actual lip movements of arbitrary identities in dynamic, unconstrained talking face videos, resulting in significant parts of the video being out-of-sync with the newly chosen audio.
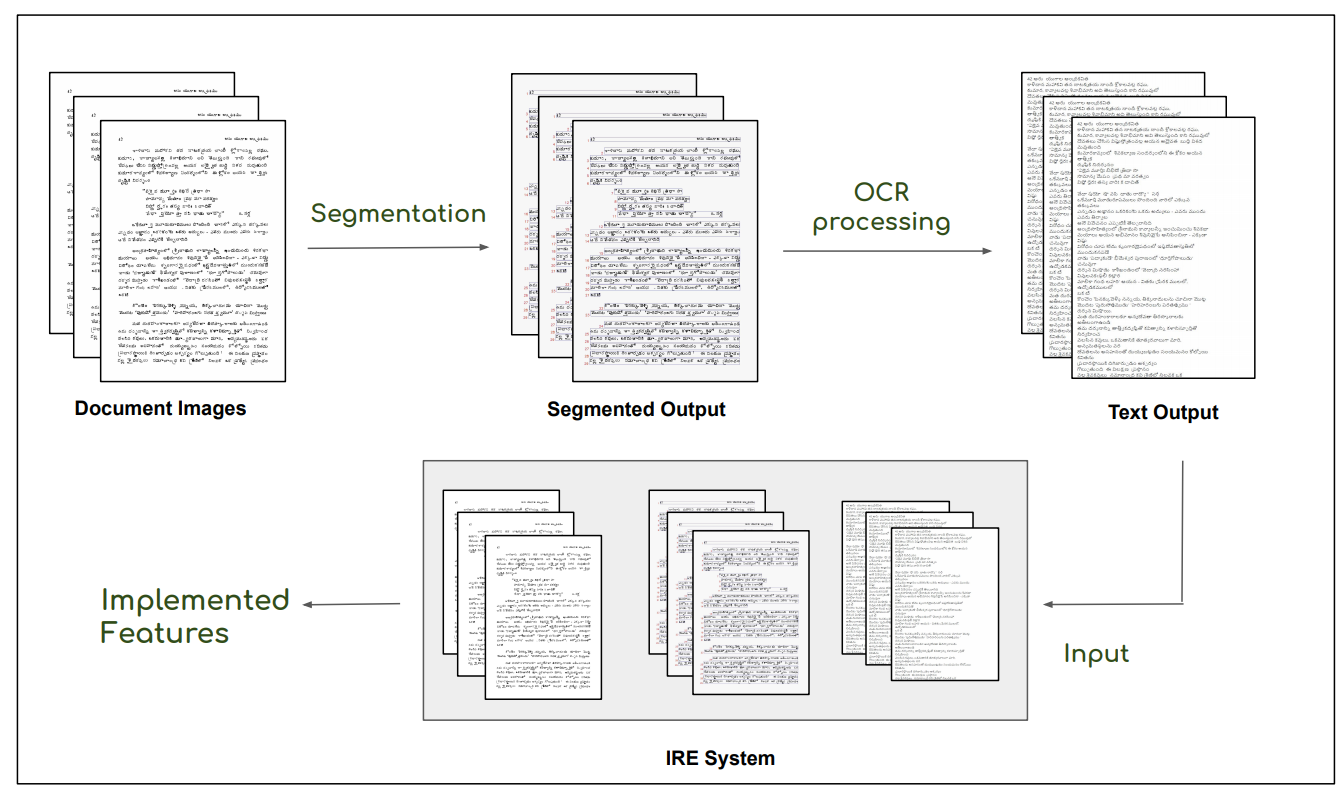 Retrieval from Large Document Image Collections
Retrieval from Large Document Image Collections
People Involved : Riya Gupta and C.V. Jawahar
Extracting the relevant information out of a large number of documents is quite a challenging and tedious task. he quality of results generated by the traditionally available full-text search engine and text-based image retrieval systems is not very optimal.
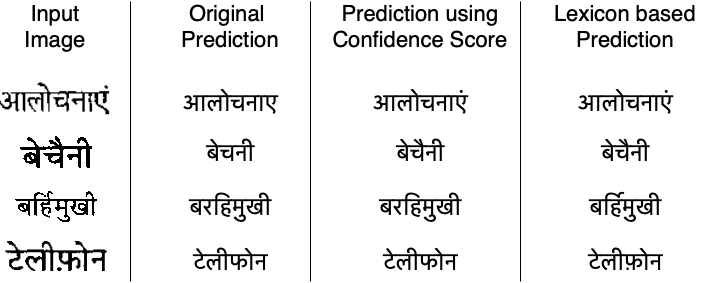 Fused Text Recogniser and Deep Embeddings Improve Word Recognition and Retrieval
Fused Text Recogniser and Deep Embeddings Improve Word Recognition and Retrieval
People Involved :Siddhant Bansal, Praveen Krishnan and C. V. Jawahar
Recognition and retrieval of textual content from the large document collections have been a powerful use case for the document image analysis..
 RoadText-1K: Text Detection & Recognition Dataset for Driving Videos
RoadText-1K: Text Detection & Recognition Dataset for Driving Videos
People Involved :Sangeeth Reddy, Minesh Mathew, Lluis Gomez, Marçal Rusinol, Dimosthenis Karatzas, and C. V. Jawahar
Perceiving text is crucial to understand semantics of outdoor scenes and hence is a critical requirement to build intelligent systems for driver assistance and self-driving. Most of the existing datasets for text detection and recognition comprise still images and are mostly compiled keeping text in mind.
 Text-to-Speech Dataset for Indian Languages
Text-to-Speech Dataset for Indian Languages
People Involved : Nimisha Srivastava, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Prajwal K R and C.V. Jawahar
India is a country where several tens of languages are spoken by over a billion strong population. Text-to-speech systems for such languages will thus be extremely beneficial for wide-spread content creation and accessibility.
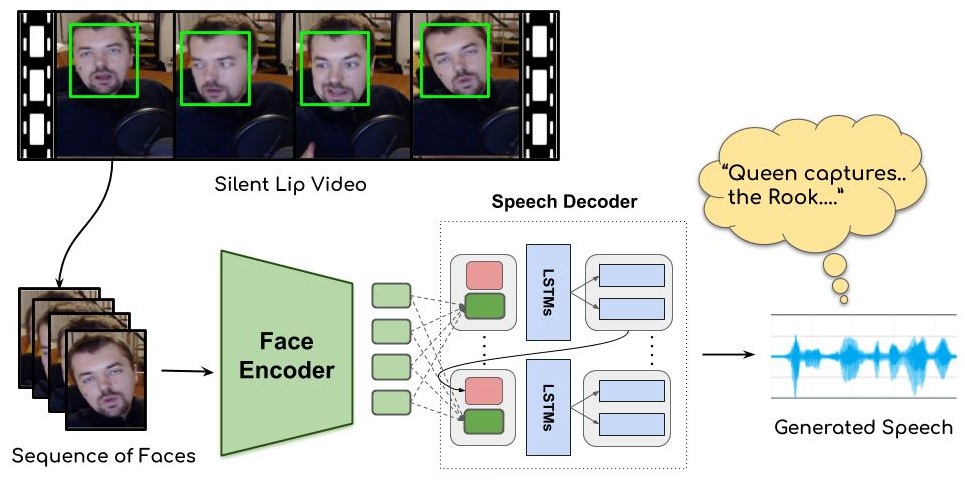 Learning Individual Speaking Styles for Accurate Lip to Speech Synthesis
Learning Individual Speaking Styles for Accurate Lip to Speech Synthesis
People Involved : Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay* Vinay Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
Humans involuntarily tend to infer parts of the conversation from lip movements when the speech is absent or corrupted by external noise. In this work, we explore the task of lip to speech synthesis,
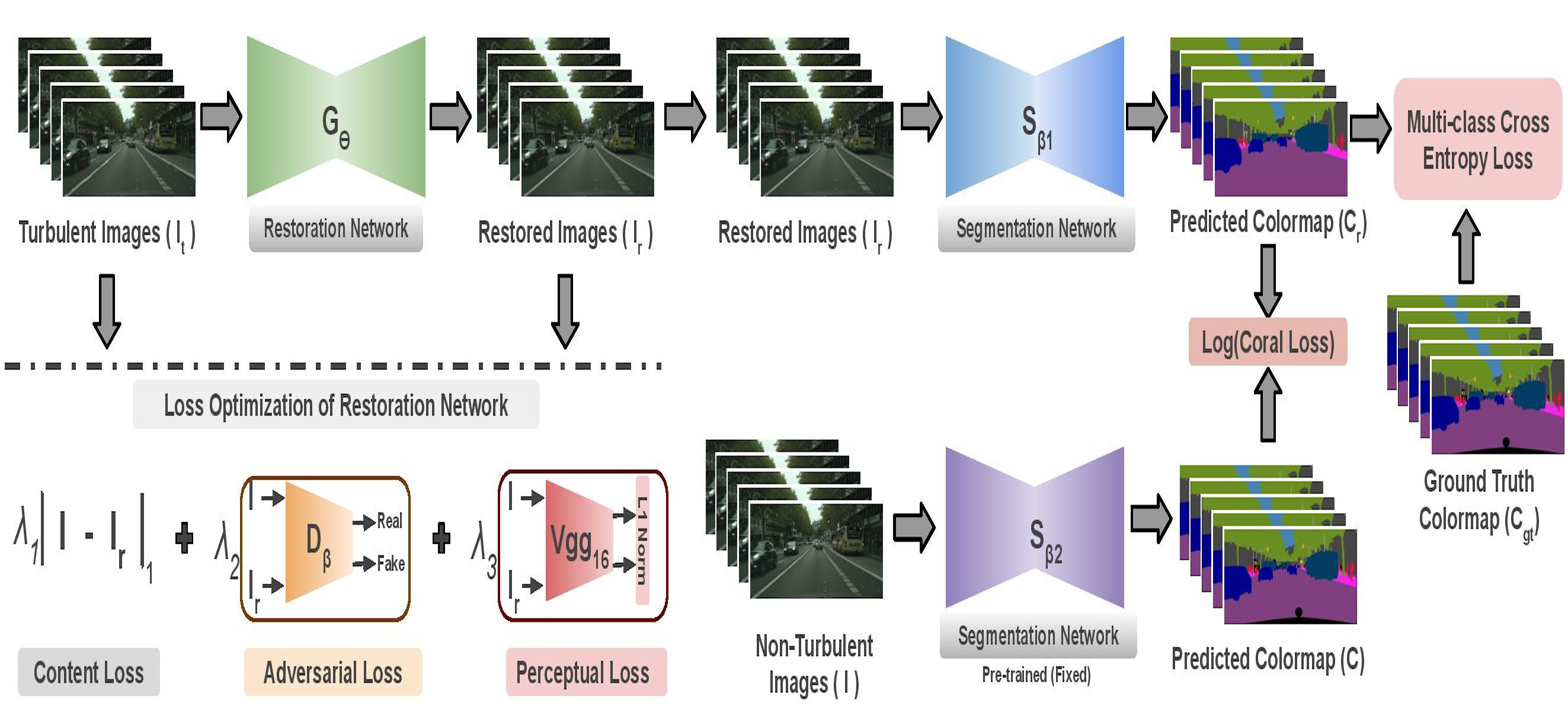 Munich to Dubai: How far is it for Semantic Segmentation?
Munich to Dubai: How far is it for Semantic Segmentation?
People Involved : Shyam Nandan Rai, Vineeth N Balasubramanian, Anbumani Subramanian and C. V. Jawahar
Cities having hot weather conditions results in geometrical distortion, thereby adversely affecting the performance of semantic segmentation model.

People Involved : Raghava Modhugu, Ranjith Reddy and C. V. Jawahar
Inspecting and assessing the quality of traffic infrastructure is a challenging task due to the massive length of roads and the regular frequency at which this needs to be done. We demonstrate a scalable system that uses computer vision for automatic inspection of road infrastructure on 1500kms of roads captured in a city.
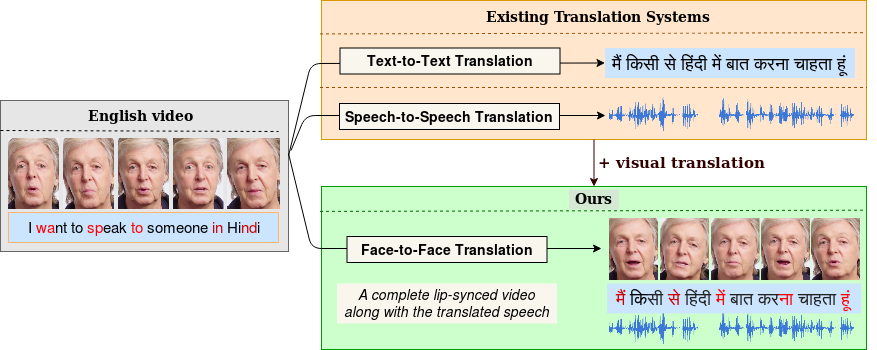 Towards Automatic Face-to-Face Translation
Towards Automatic Face-to-Face Translation
People Involved : Prajwal Renukanand, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Jerin Philip, Abhishek Jha, Vinay Namboodiri and C.V. Jawahar
In light of the recent breakthroughs in automatic machine translation systems, we propose a novel approach of what we term as "Face-to-Face Translation".
 Bringing Semantics in Word Image Representation
Bringing Semantics in Word Image Representation
People Involved : Praveen Krishnan, C. V. Jawahar
In this work, we propose two novel forms of word image semantic representations. The first form learns an inflection invariant representation, thereby focusing on the root of the word, while the second form is built along the lines of textual word embedding techniques such as Word2Vec. We observe that such representations are useful for both traditional word spotting and also enrich the search results by accounting the semantic nature of the task.

People Involved : Sudhir Yarram, Girish Varma and C. V. Jawahar
Road networks in cities are massive and is a critical component of mobility. Fast response to defects, that can occur not only due to regular wear and tear but also because of extreme events like storms, is essential. Hence there is a need for an automated system that is quick, scalable and cost- effective for gathering information about defects. We propose a system for city-scale road audit, using some of the most recent developments in deep learning and semantic segmentation. For building and benchmarking the system, we curated a dataset which has annotations required for road defects. However, many of the labels required for road audit have high ambiguity which we overcome by proposing a label hierarchy
 Learning Human Poses from Actions
Learning Human Poses from Actions
People Involved : Aditya Arun, C. V. Jawahar and M. Pawan Kumar
We consider the task of learning to estimate human pose in still images. In order to avoid the high cost of full supervision, we propose to use a diverse data set, which consists of two types of annotations: (i) a small number of images are labeled using the expensive ground-truth pose; and (ii) other images are labeled using the inexpensive action label. As action information helps narrow down the pose of a human, we argue that this approach can help reduce the cost of training without significantly affecting the accuracy.
 LectureVideoDB - A dataset for text detection and Recognition in Lecture Videos
LectureVideoDB - A dataset for text detection and Recognition in Lecture Videos
People Involved : Kartik Dutta, Minesh Mathew, Praveen Krishnan and CV Jawahar
Lecture videos are rich with textual information and to be able to understand the text is quite useful for larger video understanding/analysis applications. Though text recognition from images have been an active research area in computer vision, text in lecture videos has mostly been overlooked. In this work, we investigate the efficacy of state-of-the art handwritten and scene text recognition methods on text in lecture videos
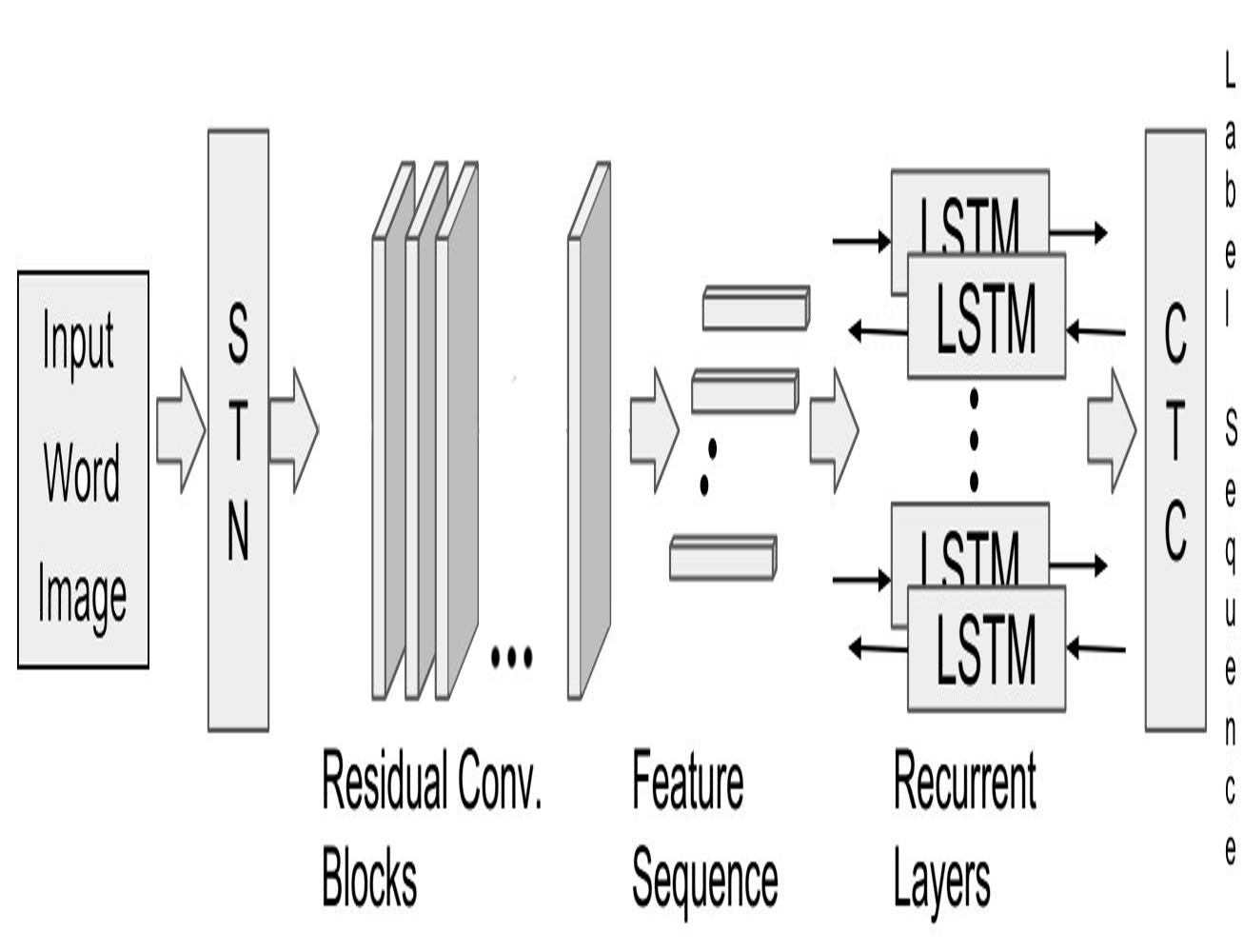 Word level Handwritten datasets for Indic scripts
Word level Handwritten datasets for Indic scripts
People Involved : Kartik Dutta, Praveen Krishnan, Minesh Mathew and CV Jawahar
Handwriting recognition (HWR) in Indic scripts is a challenging problem due to the inherent subtleties in the scripts, cursive nature of the handwriting and similar shape of the characters. Lack of publicly available handwriting datasets in Indic scripts has affected the development of handwritten word recognizers. In order to help resolve this problem, we release 2 handwritten word datasets: IIIT-HW-Dev, a Devanagari dataset and IIIT-HW-Telugu, a Telugu dataset.
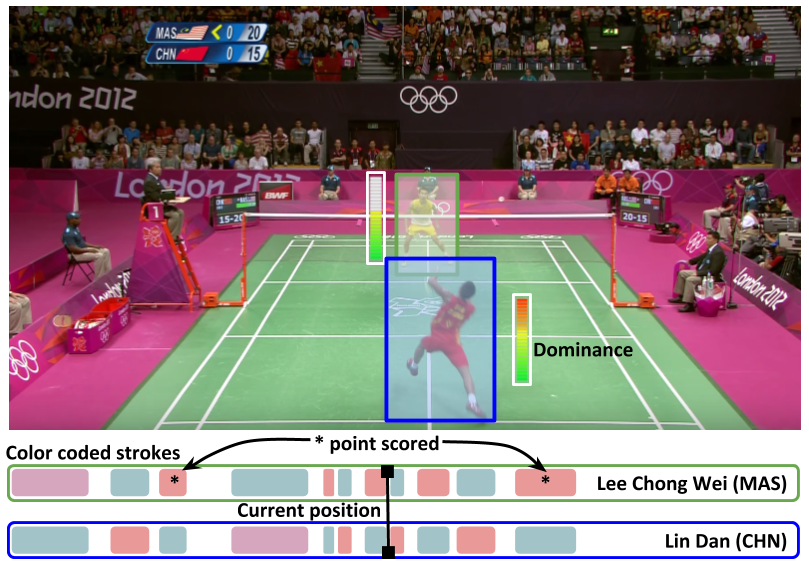 Towards Structured Analysis of Broadcast Badminton Videos
Towards Structured Analysis of Broadcast Badminton Videos
People Involved :Anurag Ghosh, Suriya Singh and C. V. Jawahar
Sports video data is recorded for nearly every major tournament but remains archived and inaccessible to large scale data mining and analytics. It can only be viewed sequentially or manually tagged with higher-level labels which is time consuming and prone to errors. In this work, we propose an end-to-end framework for automatic attributes tagging and analysis of sport videos.
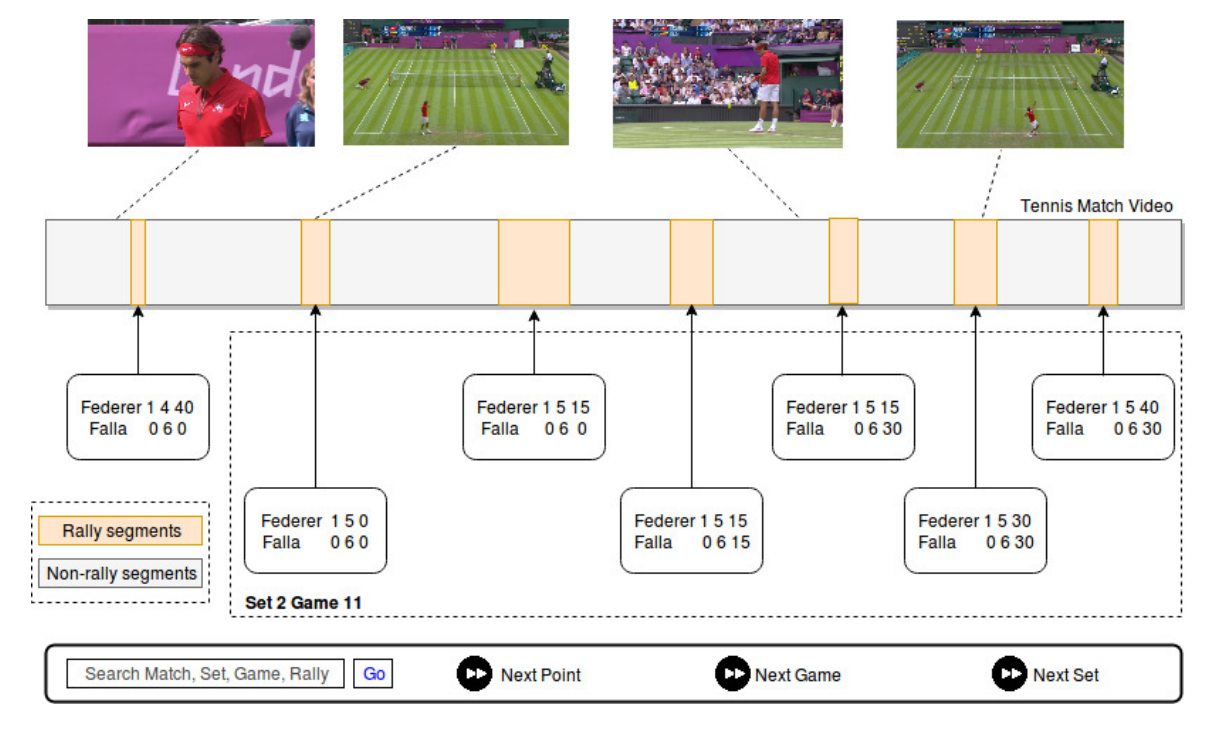 SmartTennisTV: Automatic indexing of tennis videos
SmartTennisTV: Automatic indexing of tennis videos
People Involved :Anurag Ghosh and C. V. Jawahar
In this paper, we demonstrate a score based indexing approach for tennis videos. Given a broadcast tennis video (BTV), we index all the video segments with their scores to create a navigable and searchable match. Our approach temporally segments the rallies in the video and then recognizes the scores from each of the segments, before refining the scores using the knowledge of the tennis scoring system
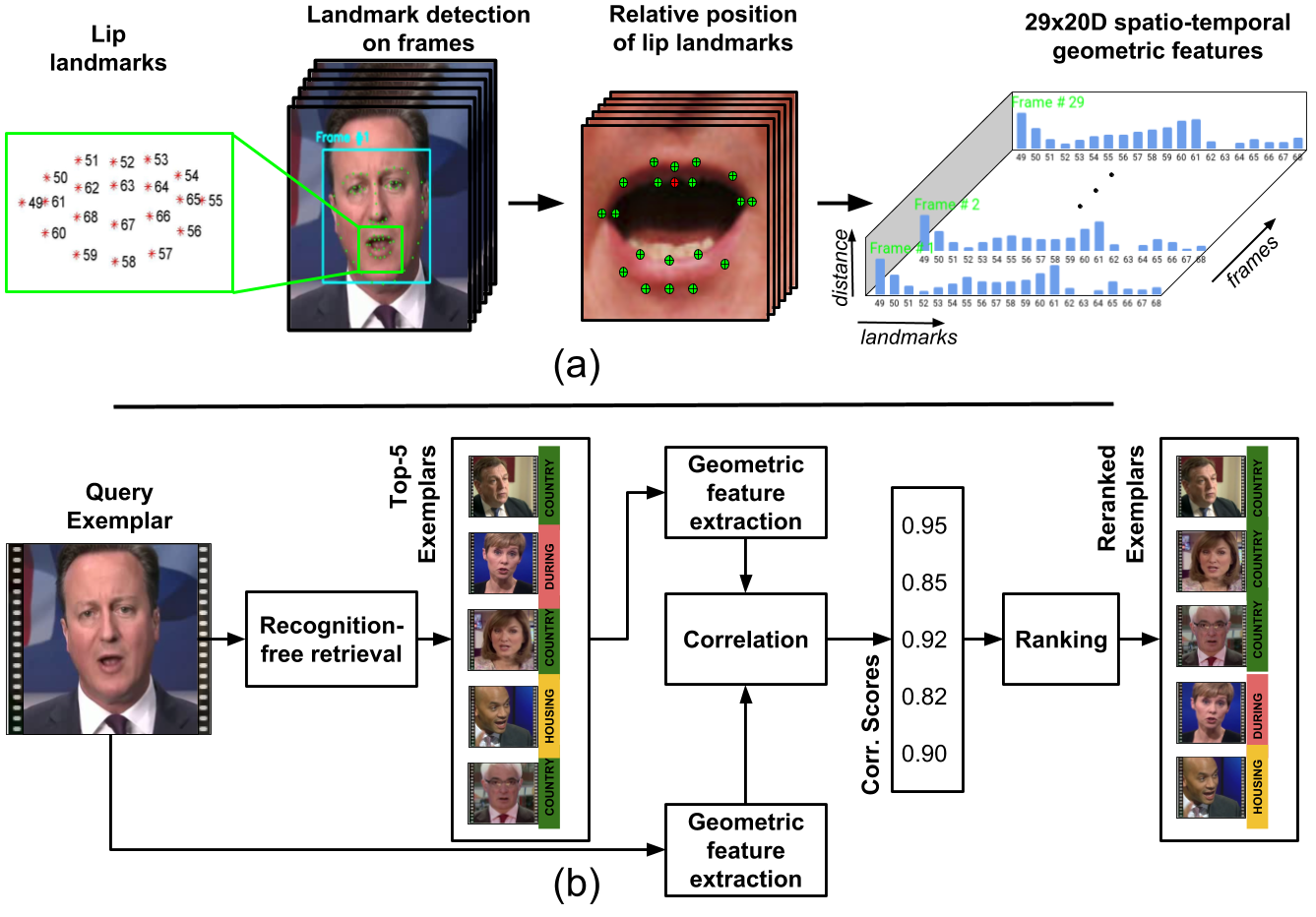 Word Spotting in Silent Lip Videos
Word Spotting in Silent Lip Videos
People Involved :Abhishek Jha, Vinay Namboodiri and C. V. Jawahar
Our goal is to spot words in silent speech videos without explicitly recognizing the spoken words, where the lip motion of the speaker is clearly visible and audio is absent. Existing work in this domain has mainly focused on recognizing a fixed set of words in word-segmented lip videos, which limits the applicability of the learned model due to limited vocabulary and high dependency on the model's recognition performance.
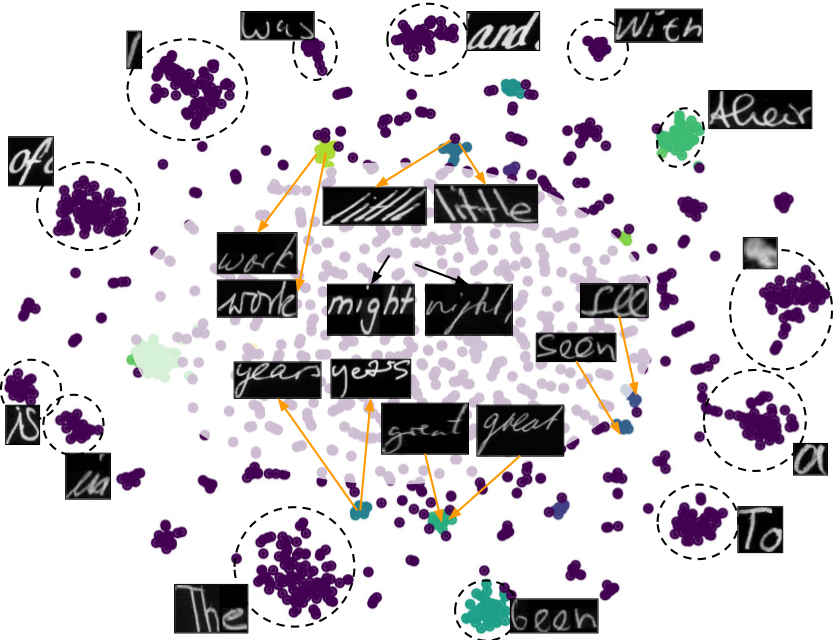 HWNet - An Efficient Word Image Representation for Handwritten Documents
HWNet - An Efficient Word Image Representation for Handwritten Documents
People Involved : Praveen Krishnan, C. V. Jawahar
We propose a deep convolutional neural network named HWNet v2 (successor to our earlier work [1]) for the task of learning efficient word level representation for handwritten documents which can handle multiple writers and is robust to common forms of degradation and noise. We also show the generic nature of our representation and architecture which allows it to be used as off-the-shelf features for printed documents and building state of the art word spotting systems for various languages.
 Unconstrained OCR for Urdu using Deep CNN-RNN Hybrid Networks
Unconstrained OCR for Urdu using Deep CNN-RNN Hybrid Networks
People Involved : Mohit Jain, Minesh Mathew, C. V. Jawahar
Building robust text recognition systems for languages with cursive scripts like Urdu has always been challenging. Intricacies of the script and the absence of ample annotated data further act as adversaries to this task. We demonstrate the effectiveness of an end-to-end trainable hybrid CNN-RNN architecture in recognizing Urdu text from printed documents, typically known as Urdu OCR. The solution proposed is not bounded by any language specific lexicon with the model following a segmentation-free, sequence-tosequence transcription approach. The network transcribes a sequence of convolutional features from an input image to a sequence of target labels.
 Unconstrained Scene Text and Video Text Recognition for Arabic Script
Unconstrained Scene Text and Video Text Recognition for Arabic Script
People Involved : Mohit Jain, Minesh Mathew, C. V. Jawahar
Building robust recognizers for Arabic has always been challenging. We demonstrate the effectiveness of an end-to-end trainable CNN-RNN hybrid architecture in recognizing Arabic text in videos and natural scenes. We outperform previous state-of-the-art on two publicly available video text datasets - ALIF and AcTiV. For the scene text recognition task, we introduce a new Arabic scene text dataset and establish baseline results. For scripts like Arabic, a major challenge in developing robust recognizers is the lack of large quantity of annotated data. We overcome this by synthesizing millions of Arabic text images from a large vocabulary of Arabic words and phrases.
People Involved : Vijay Kumar, Anoop Namboodiri, Manohar Paluri, C. V. Jawahar
Person recognition methods that use multiple body regions have shown significant improvements over traditional face-based recognition. One of the primary challenges in full-body person recognition is the extreme variation in pose and view point. In this work, (i) we present an approach that tackles pose variations utilizing multiple models that are trained on specific poses, and combined using pose-aware weights during testing. (ii) For learning a person representation, we propose a network that jointly optimizes a single loss over multiple body regions. (iii) Finally, we introduce new benchmarks to evaluate person recognition in diverse scenarios and show significant improvements over previously proposed approaches on all the benchmarks including the photo album setting of PIPA.
 Deep Feature Embedding for Accurate Recognition and Retrieval of Handwritten Text
Deep Feature Embedding for Accurate Recognition and Retrieval of Handwritten Text
People Involved : Praveen Krishnan, Kartik Dutta and C. V. Jawahar
We propose a deep convolutional feature representation that achieves superior performance for word spotting and recognition for handwritten images. We focus on :- (i) enhancing the discriminative ability of the convolutional features using a reduced feature representation that can scale to large datasets, and (ii) enabling query-by-string by learning a common subspace for image and text using the embedded attribute framework. We present our results on popular datasets such as the IAM corpus and historical document collections from the Bentham and George Washington pages.
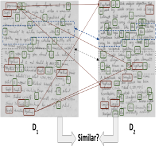 Matching Handwritten Document Images
Matching Handwritten Document Images
People Involved : Praveen Krishnan and C. V. Jawahar
We address the problem of predicting similarity between a pair of handwritten document images written by different individuals. This has applications related to matching and mining in image collections containing handwritten content. A similarity score is computed by detecting patterns of text re-usages between document images irrespective of the minor variations in word morphology, word ordering, layout and paraphrasing of the content.
 Visual Aesthetic Analysis for Handwritten Document Images
Visual Aesthetic Analysis for Handwritten Document Images
People Involved : Anshuman Majumdar, Praveen Krishnan and C. V. Jawahar
We present an approach for analyzing the visual aesthetic property of a handwritten document page which matches with human perception. We formulate the problem at two independent levels: (i) coarse level which deals with the overall layout, space usages between lines, words and margins, and (ii) fine level, which analyses the construction of each word and deals with the aesthetic properties of writing styles. We present our observations on multiple local and global features which can extract the aesthetic cues present in the handwritten documents.
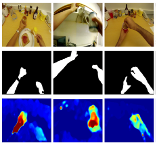 First Person Action Recognition
First Person Action Recognition
People Involved : Suriya Singh, Chetan Arora, C. V. Jawahar
 Face Fiducial Detection by Consensus of Exemplars
Face Fiducial Detection by Consensus of Exemplars
People Involved : Mallikarjun B R, Visesh Chari, C. V. Jawahar , Akshay Asthana
An exemplar based approach to detect the facial landmarks. We show that by using a very simple SIFT and HOG based descriptor, it is possible to identify the most accurate fiducial outputs from a set of results produced by regression and mixture of trees based algorithms (which we call candidate algorithms) on any given test image. Our approach manifests as two algorithms, one based on optimizing an objective function with quadratic terms and the other based on simple kNN.
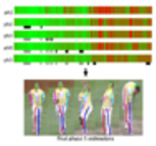 Fine-Tuning Human Pose Estimation in Videos
Fine-Tuning Human Pose Estimation in Videos
People Involved :Digvijay Singh, Vineeth Balasubramanian, C. V. Jawahar
A semi-supervised self-training method for fine-tuning human pose estimations in videos that provides accurate estimations even for complex sequences.
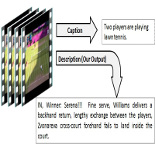 Fine-Grained Descriptions for Domain Specific Videos
Fine-Grained Descriptions for Domain Specific Videos
People Involved :Mohak Kumar Sukhwani, C. V. Jawahar
Generation of human like natural descriptions for multimedia content pose an interesting challenge for vision community. In our current work we tackle the challenge of generating descriptions for the videos. The proposed method demonstrates considerable success in generating syntactically and pragmatically correct text for lawn tennis videos and is notably effective in capturing majority of the video content. Unlike any previous work our method focuses on generating exhaustive and richer human like descriptions. We aim to provide reliable descriptions that facilitate the task of video analysis and help understand the ongoing events in the video. Large volumes of text data are used to compute associated text statistics which is thereafter used along with computer vision algorithms to produce relevant descriptions
 Learning relative attributes using parts
Learning relative attributes using parts
People Involved :Ramachandruni N Sandeep, Yashaswi Verma, C. V. Jawahar
Our aim is to learn relative attributes using local parts that are shared across categories. First, instead of using a global representation, we introduce a part-based representation combining a pair of images that specifically compares corresponding parts. Then, with each part we associate a locally adaptive “significance coefficient” that represents its discriminative ability with respect to a particular attribute. For each attribute, the significance-coefficients are learned simultaneously with a max-margin ranking model in an iterative manner. Compared to the baseline method , the new method is shown to achieve significant improvements in relative attribute prediction accuracy. Additionally, it is also shown to improve relative feedback based interactive image search.
 Decomposing Bag of Words Histograms
Decomposing Bag of Words Histograms
People Involved :Ankit Gandhi, Karteek Alahari, C V Jawahar
We aim to decompose a global histogram representation of an image into histograms of its associated objects and regions. This task is formulated as an optimization problem, given a set of linear classifiers, which can effectively discriminate the object categories present in the image. Our decomposition bypasses harder problems associated with accurately localizing and segmenting objects.
 Action Recognition using Canonical Correlation Kernels
Action Recognition using Canonical Correlation Kernels
People Involved :G Nagendar, C V Jawahar
Action recognition has gained significant attention from the computer vision community in recent years. This is a challenging problem, mainly due to the presence of significant camera motion, viewpoint transitions, varying illumination conditions and cluttered backgrounds in the videos. A wide spectrum of features and representations has been used for action recognition in the past. Recent advances in action recognition are propelled by (i) the use of local as well as global features, which have significantly helped in object and scene recognition, by computing them over 2D frames or over a 3D video volume (ii) the use of factorization techniques over video volume tensors and defining similarity measures over the resulting lower dimensional factors. In this project, we try to take advantages of both these approaches by defining a canonical correlation kernel that is computed from tensor representation of the videos. This also enables seamless feature fusion by combining multiple feature kernels.
People Involved :Yashaswi Verma, C V Jawahar
In many real-life scenarios, an object can be categorized into multiple categories. E.g., a newspaper column can be tagged as "political", "election", "democracy"; an image may contain "tiger", "grass", "river"; and so on. These are instances of multi-label classification, which deals with the task of associating multiple labels with single data. Automatic image annotation is a multi-label classification problem that aims at associating a set of text with an image that describes its semantics.
People Involved :Udit Roy, Anand Mishra, Karteek Alahari and C.V. Jawahar
Scene text recognition has gained significant attention from the computer vision community in recent years. Often images contain text which gives rich and useful information about their content. Recognizing such text is a challenging problem, even more so than the recognition of scanned documents. Scene text exhibits a large variability in appearances, and can prove to be challenging even for the state-of-the-art OCR methods. Many scene understanding methods recognize objects and regions like roads, trees, sky etc in the image successfully, but tend to ignore the text on the sign board. Our goal is to fill this gap in understanding the scene.
 Semantic Classification of Boundaries of an RGBD Image
Semantic Classification of Boundaries of an RGBD Image
People Involved :Nishit Soni, Anoop M. Namboodiri, C. V. Jawahar, Srikumar Ramalingam
 Fine-Grain Annotation of Cricket Videos
Fine-Grain Annotation of Cricket Videos
People Involved : Rahul Anand Sharma, Pramod Sankar K, C. V. Jawahar

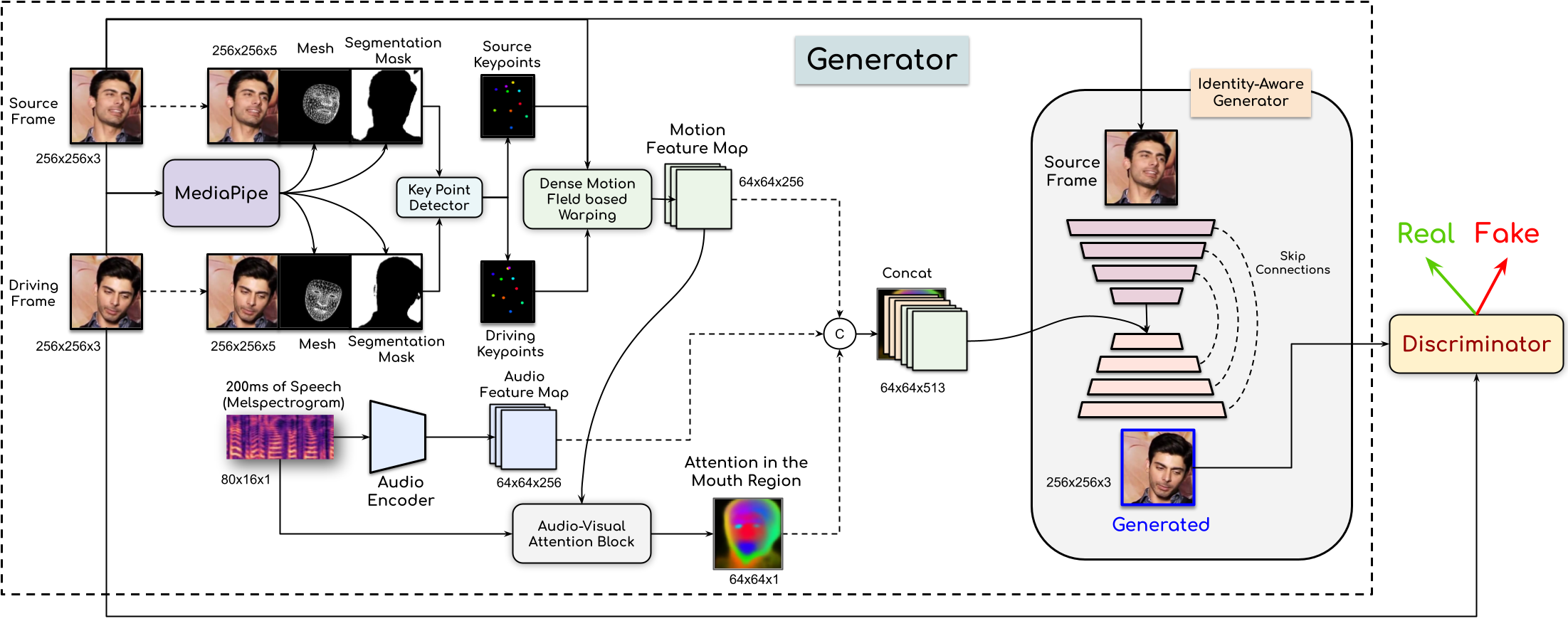
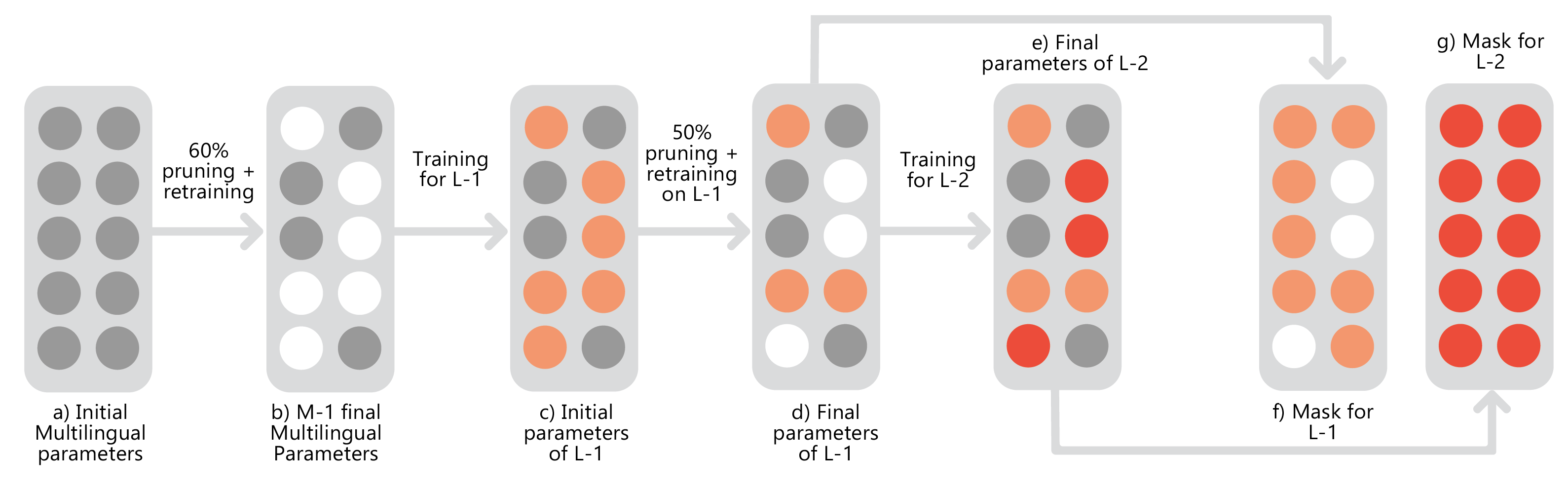

 Image Annotation
Image Annotation Scene Text Understanding
Scene Text Understanding